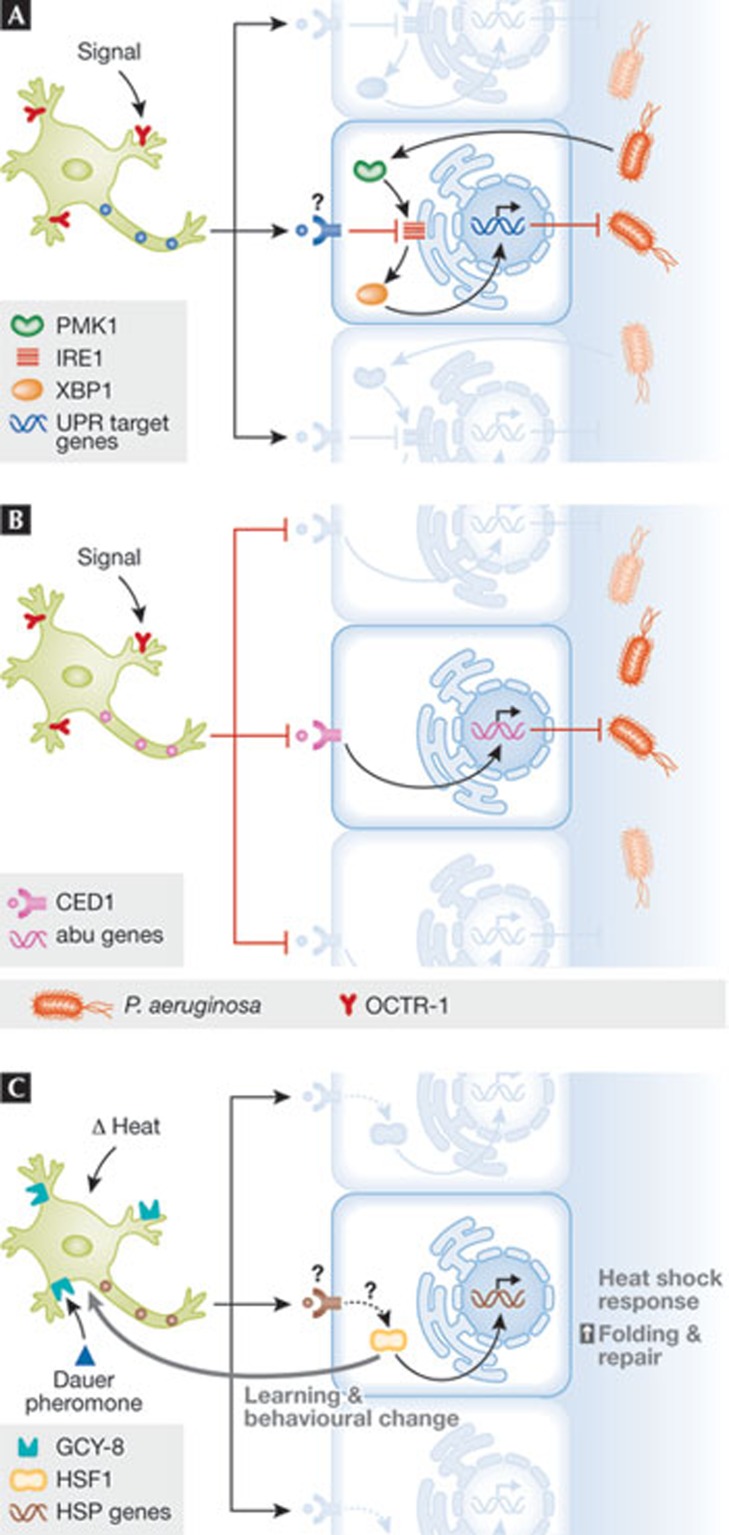
Figure 1.
Cell-nonautonomous control of the UPR and HSR. (A) Organismal control of UPR responses in peripheral tissue by the nervous system in adult Caenorhabditis elegans. The activity of OCTR-1, expressed in sensory neurons, represses the IRE1/XBP1 pathway, modulating innate immunity. PMK-1 might also modulate this pathway. (B) A related pathway also operates to control innate immunity during C. elegans development, involving the direct regulation of a non-canonical UPR response (abu genes). This pathway might be regulated by the phagocytic receptor CED-1, and does not engage a classical UPR response. (C) The HSR is negatively regulated by thermosensory neurons though GCY-8 and is modulated by the dauer pheromone. A feedback loop from peripheral tissue to sensory neurons modulates behavioural responses against fluctuations in body temperature. CED-1, cell death abnormal 1; GCY-8, guanylyl cyclase 8; HSR, heat shock response; IRE1, inositol-requiring enzyme 1; OCTR-1, octopamine receptor 1; PMK-1, mitogen-activated kinase 1; UPR, unfolded protein response; XBP1, X-box binding protein 1.