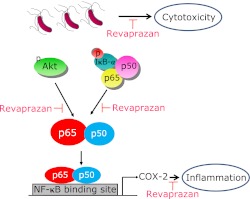
Fig. 4.
A putative molecular mechanism showing the inhibition of H. pylori-induced COX-2 expression with revaprazan. Revaprazan, a novel acid pump antagonist, exerted COX-2 inhibition led by the inactivation of Akt signaling and NF-κB-DNA binding actions. Therefore, even though revaprazane is acid suppressant playing as acid pump antagonist, it can additionally impose the direct anti-inflammatory actions in H. pylori-associated gastric inflammation as well as rescuing stomach from H. pylori-induced cytotoxicity.