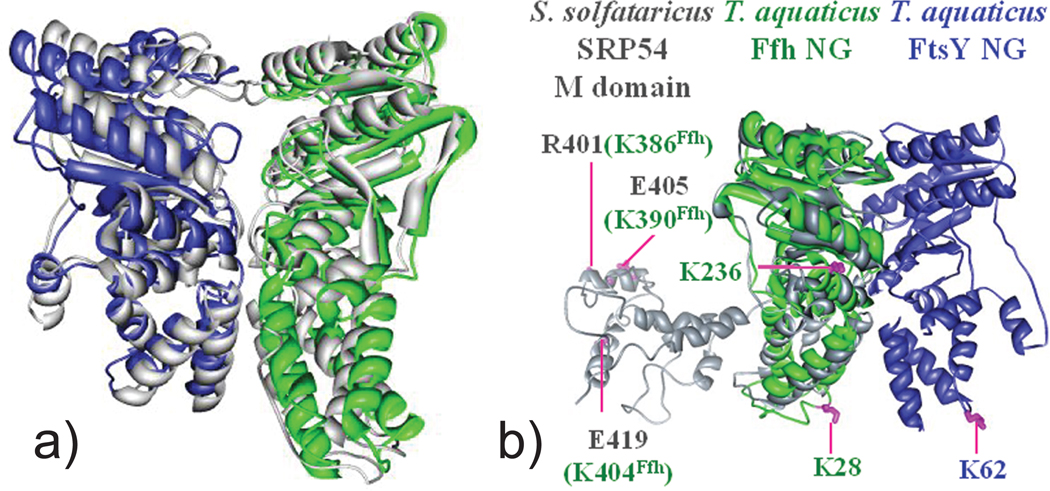
Figure 7.
(a) The model of T. aquaticus Ffh-FtsY NG complex was created by docking the apo-NG domains of Ffh (green) and FtsY (blue) according to crosslinking constraints.218 The MS3D model overlays perfectly with the crystal structure (grey) of the complex. (b) The structure of S. solfataricus SRP54 (gray) was superimposed with T. aquaticus Ffh (green) to generate a model for the Ffh_FtsY complex including the M domain. Relative positions of T. aquaticus lysine residues in the SRP54 M domain are mapped (green). These residues formed crosslinks with residues G(−3) and K62 of FtsY (magenta line), suggesting a close proximity of the M domain to the Ffh-FtsY complex interface. Adapted with permission from reference 218.