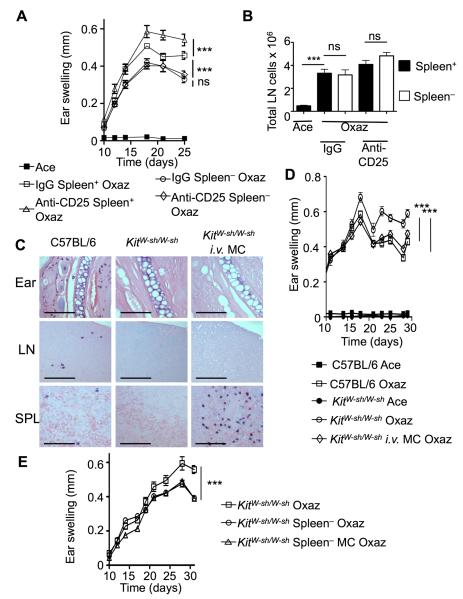
Figure 3. The spleen exacerbates dermatitis and facilitates anti-CD25 enhancement or MC suppression of disease.
(A) Splenectomized (Spleen−) C57BL/6 (WT) mice (n = 5) were treated with either control IgG or anti-CD25 and with oxazolone to induce dermatitis. Ear swelling was compared to non-splenectomized (Spleen+) littermates. (B) Draining cervical LNs were harvested for evaluation of total cell numbers. The LNs were extracted from normal and splenectomized mice shown in (A) after full treatment with acetone or oxazolone. (C) MCs were introduced through the tail-vein prior to induction of oxazolone-dermatitis, and tissues from the inflamed ear, draining lymph nodes (LN) and spleens (SPL) were stained with toluidine blue. Scale bars represent 100 μm. (D) Disease course in WT, KitW-sh/W-sh or KitW-sh/W-sh following i.v. injection of MCs (n = 5). Two independent experiments were conducted. (E) Comparison of ear swelling between KitW-sh/W-sh mice and KitW-sh/W-sh following splenectomy or splenectomy and i.d. MC reconstitution (n = 5). Statistical analysis was done by a two-way ANOVA test (A, B, D and E) or by a two-tailed student’s t test (B lower panels). Results are means + SEM. ***p<0.001. See also Figures S3 and S5.