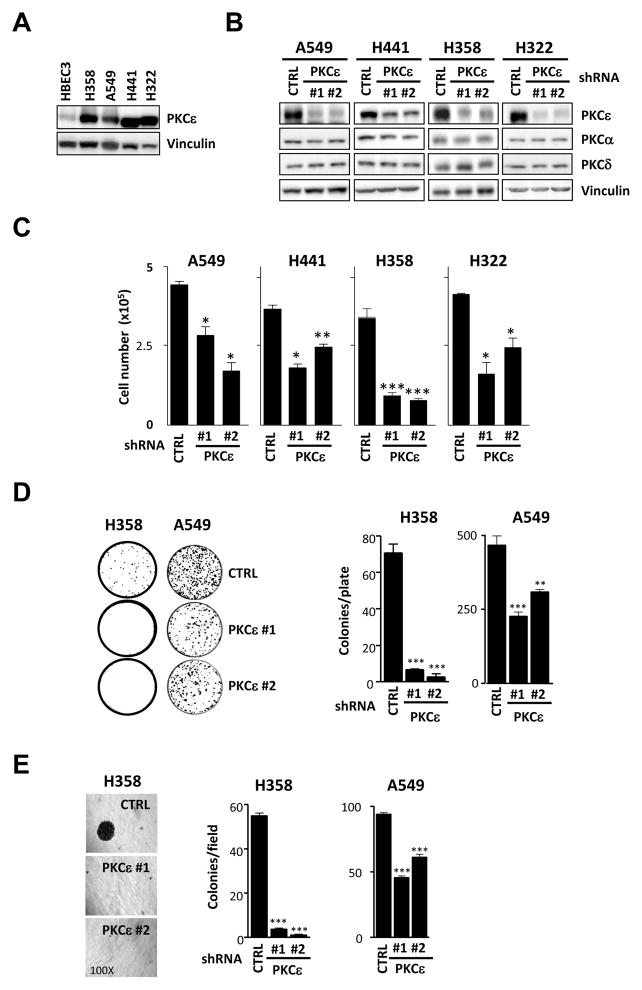
Fig. 1. PKCε is required for the growth of NSCLC cells.
A) PKCε expression was analyzed by Western blot in immortalized non-tumorigenic (HBEC3) and NSCLC-derived cell lines (H358, H441, H322 and A549). Cells lines were obtained from ATCC and grown as recommended by the provider. An anti-PKCε antibody (Santa Cruz) was used at a 1:1000 dilution. B) Cells were infected with shRNA lentiviruses for PKCε (MISSION shRNA Lentiviral Transduction particles, Sigma, NM_005400 ε#1, clone ID x-741s1c1; ε#2, clone ID x-375s1c1) followed by selection with puromycin (1–2 μg/ml). MISSION non-target shRNA Lentiviral Transduction particles (Sigma, SHC002V) were used as control (CTRL). Expression of PKCε in NSCLC stable cell lines is depicted. C) Cells (5 ×104) were seeded in 12-well plates, allowed to grow in 2% FBS and counted 48 h later using a hemocytometer. D) For liquid colony formation assays cells were plated in 100 mm plates (100 cells/plate for H358 and 1000 cells/plate for A549). Medium was replaced twice a week and after 15 days colonies were stained with 0.7% methylene blue in 50% ethanol. E) To evaluate anchorage-independent growth 3 ×103 cells were plated in 0.35% agar over a 0.5% agar layer. After 10 days the plates were stained with MTS. For each well, the number of colonies was counted in 5 different fields and averaged. In all cases, data are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. of 3 individual experiments. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001.