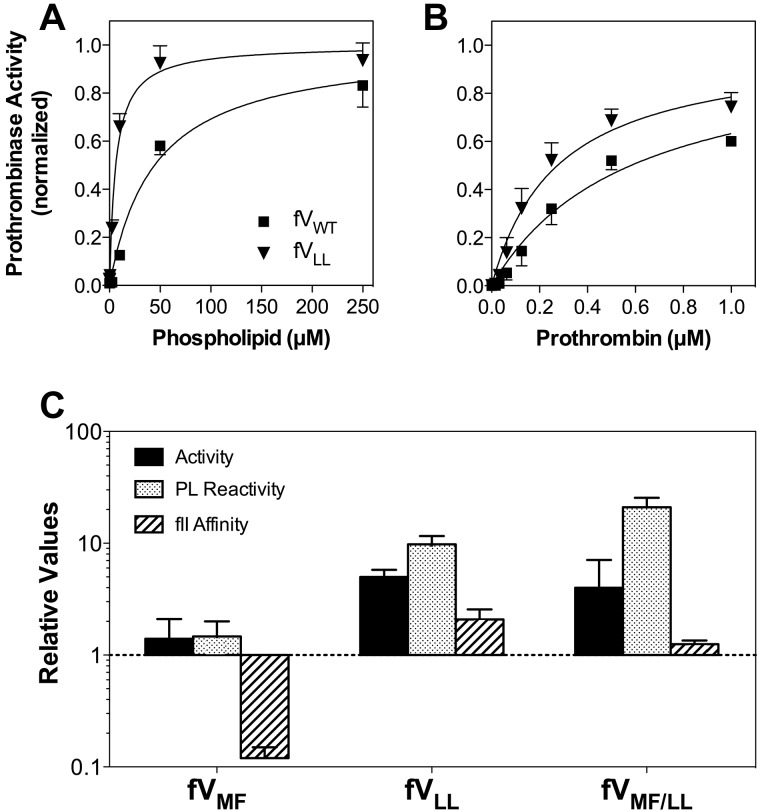
Figure 3.
Relative activities, membrane interaction, and affinities for FV mutants. (A) Membrane reactivity for FVWT (■) or FVLL (▾) was determined by mixing with FXa, prothrombin, and various concentrations of sonicated vesicles. The quantity of thrombin formed was measured with chromogenic substrate S-2238. The apparent affinity of FVLL was higher than FVWT. The vesicles had a composition of PS:PE:PC 4:20:76; concentrations of FV and mutants were 0.2nM; FXa, 2.5pM; and prothrombin, 2μM. Displayed represent the mean ± SEM, fitted to a single-site binding model (smooth curves). (B) Apparent FXa affinity was determined as in panel A, except that the phospholipid concentration was held constant (50μM) and the FXa concentration was varied. (C) Apparent KM for the FVa-FXa complex was determined as in panel A, except that the phospholipid concentration was constant and the prothrombin concentration varied. (A-C) Fitted results were normalized to the Bmax value for each curve to optimize comparison of the relative affinities. (D) The specific activities, phospholipid vesicle reactivity, apparent FXa affinities, and apparent prothrombin affinities (KM) for each mutant are displayed with reference to control experiments performed with wild-type FV (as in panels A-C for FVLL). The displayed values represent the mean ± SEM. Each fit was performed on a minimum of 3 separate experiments, each performed in duplicate.