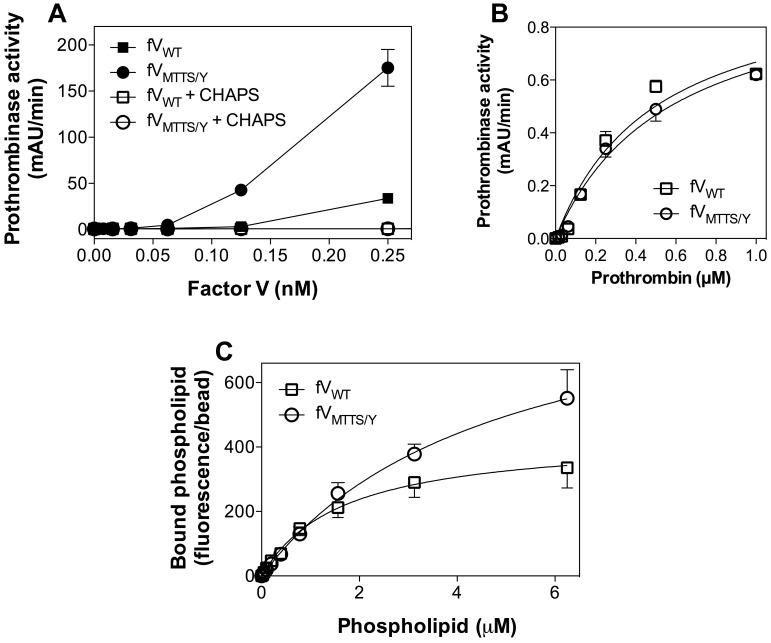
Figure 6.
Membrane-independent activity, apparent prothrombin and FXa affinities, and phospholipid binding affinity of FVMTTS/Y. (A) Various concentrations of FVWT or FVMTTS/Y with or without a 1% CHAPS wash during purification were mixed with FXa (0.4nM) and prothrombin (1μM) in the absence of phospholipid vesicles. Washing with 1% CHAPS during purification abolished all apparent lipid-independent activity. (B) Apparent KM for the prothrombinase complex with mutant or WT CHAPS-washed FV was determined with saturating concentrations of vesicles of composition 4:20:76 (PS:PE:PC). FVMTTS/Y showed the same apparent affinity for prothrombin as FVWT. Values represent mean ± SEM for at least 2 experiments, each performed in duplicate. (C) Direct affinity for phospholipid vesicles was evaluated for FVWT or FVMTTS/Y by immobilizing FV to mAb CBC-MOR101 covalently linked to Superose beads. Beads were incubated overnight with either FVWT or FVMTTS/Y and then mixed with various concentrations of fluorescein-labeled vesicles of composition 4:5:20:71 (PS:PE-CF:PE:PC). After 30 minutes, the quantity of vesicles bound to FVWT or FVMTTS/Y was measured by flow cytometry. The vesicle dissociation constants were 4.8 ± 1.1μM for FVMTTS/Y and 1.7 ± 0.4μM for FVWT. Data represent the mean ± SEM for at least 4 experiments.