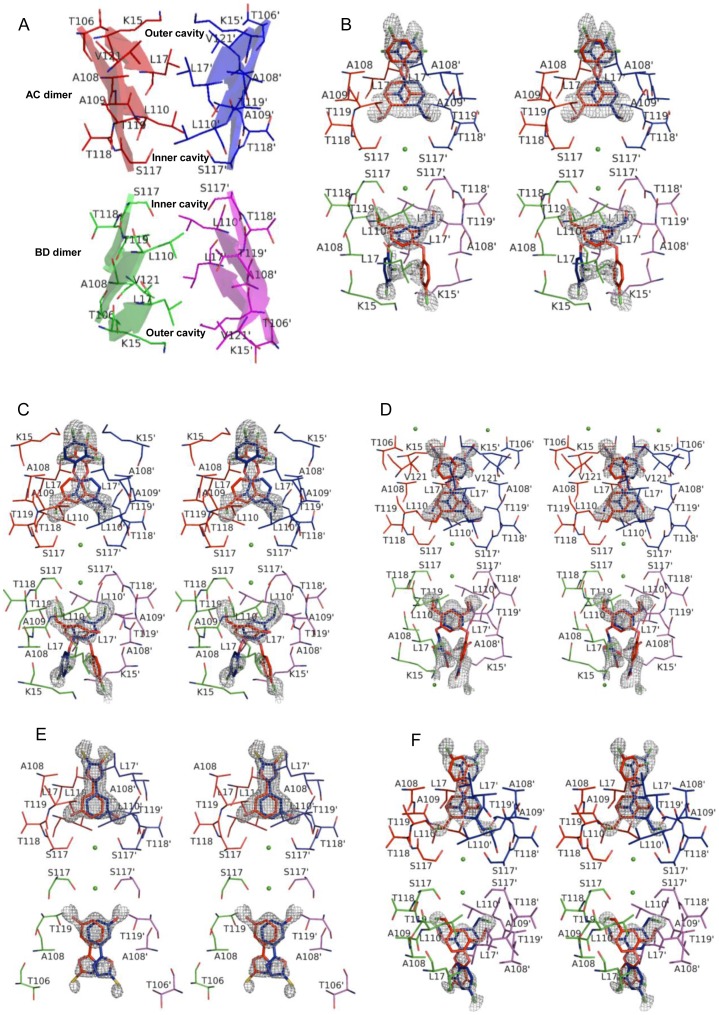
Figure 3. Crystal structures of TTR-ligand complexes.
Two T4 (thyroxine) binding sites are shown with the bound ligand in each case. Interacting residues and the chemical structures of the bound ligands are shown as thin and thick sticks, respectively. The two T4 binding sites can be found at the interface of the AC and BD dimers. The portion of TTR dimers involved in making the T4 sites are shown as transparent cartoon and monomer A, B, C, and D are colored as red, green, blue and magenta, respectively. Stereo representation of all structures is shown and the TTR amino acid residues that contact ligands are shown as sticks and labelled in each case. The difference maps calculated for the ligand are contoured at σ = 3.0. Ligands binds in the two T4 binding sites, each ligand (red) generates a symmetric copy of itself (blue) which appears superimposed on it owing to its positioning on the twofold symmetric axis. Primed amino acids refer to symmetry related monomers of TTR. (A) Schematic of the two T4 binding sites without the ligand highlighting the residues forming the inner and outer binding cavities; (B) wtTTR-C2; (C) wtTTR-C3; (D) wtTTR-C6; (E) wtTTR-C1; (F) wtTTR-C7.