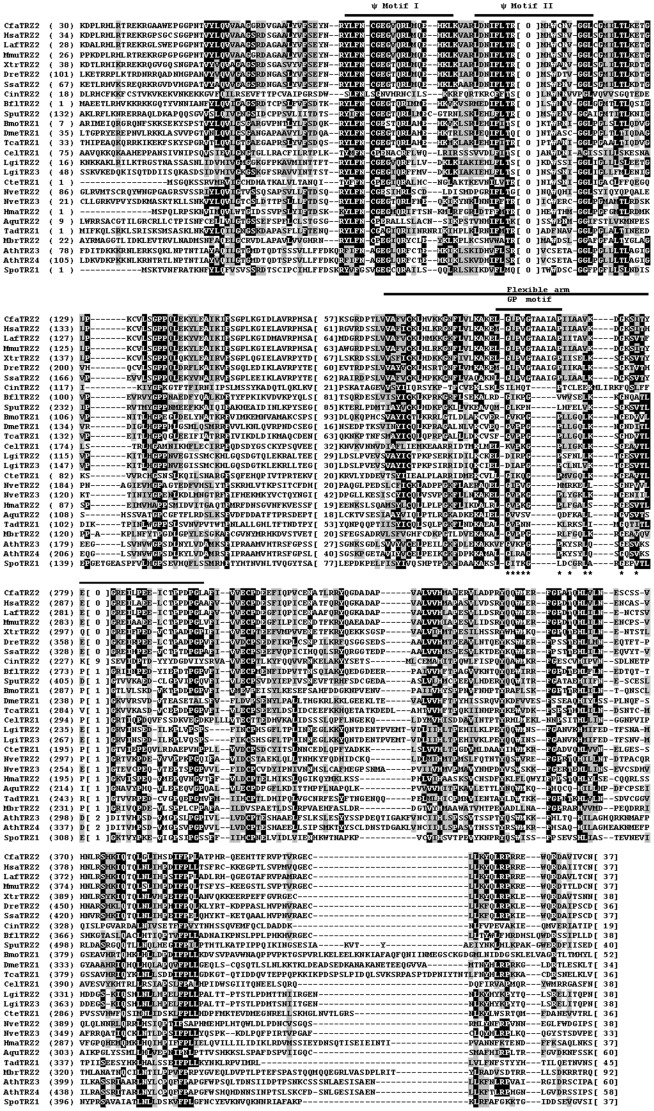
Figure 3. Multiple sequence alignment of representatives of N-terminal halves of the metazoan and non-metazoan tRNase ZLs.
Representative metazoan tRNase ZLs are from ten deuteromes including C. familiaris (Cfa), H. sapiens (Hsa), L. Africana (Laf), M. musculus (Mmu), X. tropicalis (Xtr), D. rerio (Dre), S. salar (Ssa), C. intestinalis (Cin), B. floridae (Bfl), and S. purpuratus (Spu), six protostomes including B. mori (Bmo), D. melanogaster (Dme), T. castaneum (Tca), C. elegans (Cel), L. gigantean (Lgi), and C. teleta (Cte), and four basal metazoans including N. vectensis (Nve), H. magnipapillata (Hma), A. queenslandica (Aqu), and T. adhaerens (Tad). Non-metazoan tRNase ZLs are from the unicellular choanoflagellate M. brevicollis (Mbr), green plant A. thaliana (Ath) and fungal S. pombe (Spo). See Table 1 for more information. The alignment was constructed using the computer program Clustal W [52]. Identical residues are on a black ground and conserved residues shaded in gray. The conserved motifs of tRNase Zs indicated above the alignment are labeled according to references [17], [19], [58]. The numbers in brackets indicate the length of the region in the protein, which are species-specific and could not be correctly aligned. Hyphens represent gaps introduced into sequences for maximum alignment. Amino acid residues predicted to be critical for activity are indicated by a star.