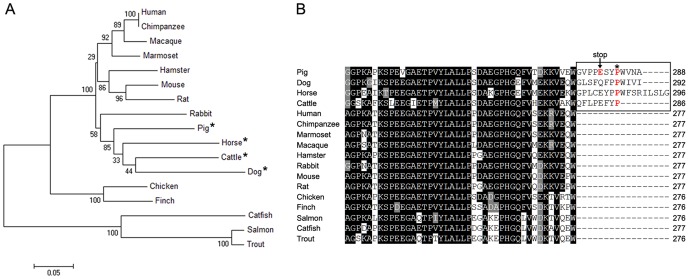
Figure 4. Phylogenetic comparison of PTCR homologs from various organisms.
(A) Phylogenetic tree of PTCR homologs. The phylogenetic tree was constructed using the neighbor-joining method and visualized using MEGA4 software. GenBank accession numbers of PTCR homologs are as follows: catfish (ADO28395), cattle (NP_001030258), chicken (NP_001025966), chimpanzee (XP_531449), dog (XP_535589), finch (XP_002187585), hamster (BAB62840), horse (XP_001493595), human (NP_001748), macaque (BAB97216), marmoset (XP_002761453), mouse (NP_031646), pig (NP_999238), rabbit (NP_001076218), rat (NP_062043), salmon (ACI69439), and trout (NP_001118068). Asterisks indicate carbonyl reductases possessing the additional C-terminal tail. (B) Alignment of the amino acid sequences of a C-terminal segment of PTCR homologs in (A). The box indicates additional C-terminal tails. The arrow represents the residue that mutated nonsynonymously into a stop signal in PTCR. The asterisk represents the proline residues conserved among pig, dog, horse, and cattle.