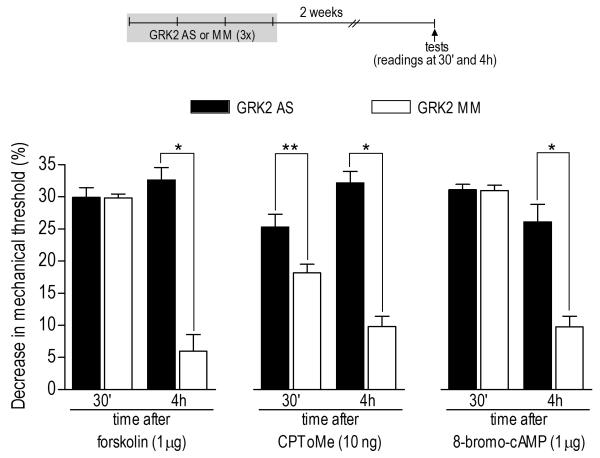
Figure 7. Prolongation of hyperalgesia induced by direct activation of intracellular second messengers by previous knockdown of GRK2.
Rats were treated with antisense (AS, black bars) or mismatch (MM, clear bars) for GRK2 for 3 consecutive days. Two weeks after ODN treatments, activators of adenyl cyclase (forskolin, 1 μg) or Epac (CPToMe, 10 ng), or the cAMP analog 8-bromo-cAMP (1 μg) were injected into the hind paw of different groups of rats. Mechanical thresholds (not significantly affected by AS- and MM-ODN treatment, data not shown), just before the injection of the second messenger activators were: forskolin/GRK2 AS: 112.3 ± 2.0 g; forskolin/GRK2 MM: 115.0 ± 2.2 g; CPToMe/GRK2 AS: 113.3 ± 3.3 g; CPToMe/GRK2 MM: 103.3 ± 2.1 g; 8-bromo-cAMP/GRK2 AS: 115.0 ± 2.2 g; 8-bromo-cAMP/GRK2 MM: 112.0 ±1.6 g. Measurements of nociceptive thresholds were performed 30 min and 4 h after the injections. Comparison between GRK2 AS- and MMODN groups at the 4th h post injections showed prolongation of hyperalgesia in all cases (GRK2 AS/forskolin at 4th h X GRK2 MM/forskolin at 4th h: *p< 0.0001; GRK2 AS/8-bromocAMP at 4th h X GRK2 MM/8-bromo-cAMP at 4th h: *p< 0.0001; GRK2 AS/CPToMe at 4th h X GRK2 MM/ CPToMe at 4th h: *p< 0.0001, unpaired Student’s t-test, N=6 per group). In addition, contrary to forskolin (p=0.9523) and 8-bromo-cAMP (p=0.8912), for CPToMe, unpaired Student’s t-test showed a significant difference, between GRK2 AS and MM groups, in the hyperalgesia 30 min after injection of lower dose of CPToMe (**p=0.0137, N=6 per group), suggesting potentiation of the effect in the GRK2 AS-treated group.