Fig. 4. Isolation of non-inactivating and inactivating voltage-gated K+ currents in small DRG neurons.
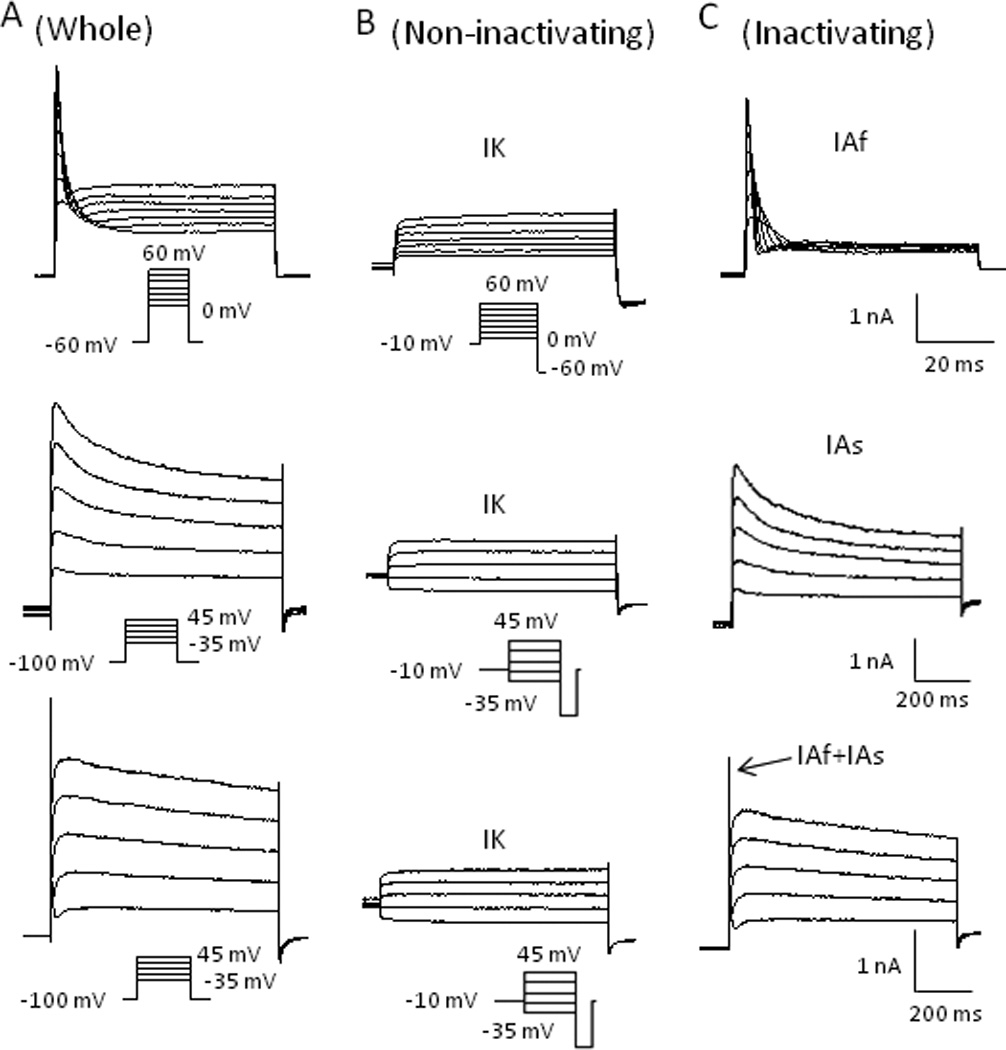
(A) Representative traces of whole outward currents from three separated cells evoked by voltage steps (shown below the traces) from a 2-second pre-potential of −60 mV (top) or −100 mV (middle and bottom). (B) Same activation steps as in A, but preceded by a 2-second pre-pulse to −10 mV to remove inactivating current component, which isolated non-inactivating K+ currents (IK currents). (C) Subtraction of non-inactivating currents from whole-currents revealed two types of inactivating K+ currents (IA currents): fast inactivating (IAf) (top) and slow inactivating (IAs) currents (middle) in two separate DRG neurons. The bottom panel shows the mixture of both IAf and IAs currents in a single DRG neuron.
