Fig. 7.
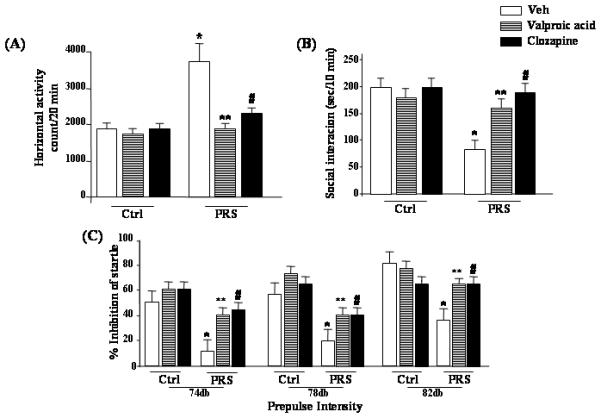
Schizophrenia-like behavioral abnormalities in PRS mice are reversed by treatment with valproic acid (70 mg/kg, i.p.; twice a day for 5 days), or clozapine (5 mg/kg, s.c.; twice a day, for 5 days). Data of locomotor activity (A), social interaction (B), and PPI (C), 24 hours after the last drug injection, are shown. One way ANOVA comparing controls (NS) veh, PRS veh, PRS VPA and PRS clozapine: (A) locomotor activity (F3,33 = 8.919, p = 0.001), (B) social interaction (F3,28 = 17.233, p < 0.001, and (C) PPI (74db F3,42 = 5.189, p = 0.004; 78db F3,42 = 9.625, p < 0.001; 82db F3,42 = 6.582, p < 0.001). Post-hoc Newman-Keuls comparisons indicated that PRS veh mice differed from controls veh mice (*), and from PRS mice treated with VPA (**) or clozapine (#). Analysis for PRS mice considered yielded a similar result while ANOVAs for controls were not significant.
