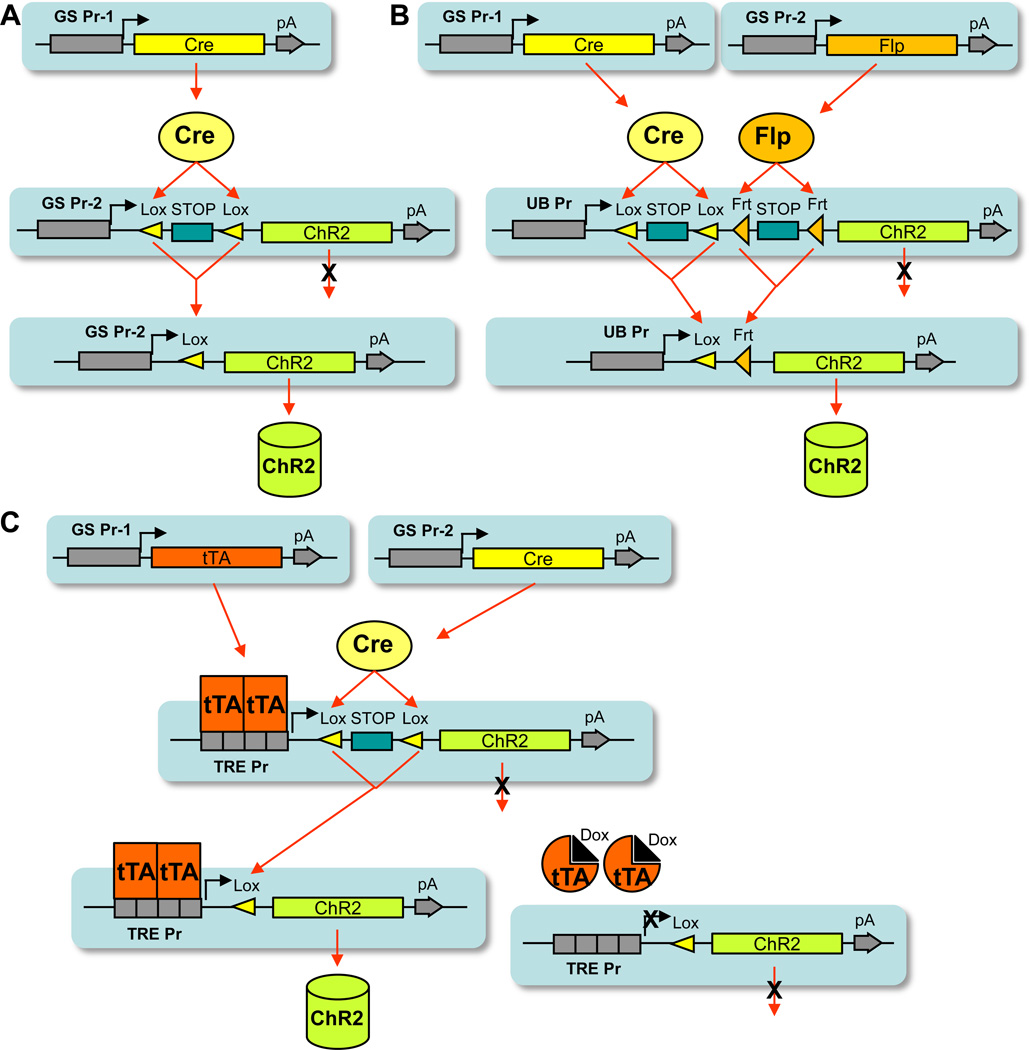
Figure 3.
The intersectional approaches to expressing optogenetic tools (using ChR2 as an example) to higher specificity. (A) A simple intersectional approach, in which the driver line uses the gene-specific promoter 1 (GS Pr-1) and the reporter line uses the gene-specific promoter 2 (GS Pr-2). (B) A Cre/Flp dual recombinase intersectional approach, in which the Cre driver line uses gene-specific promoter 1, and the Flp driver line uses gene-specific promoter 2. The double reporter line is both Cre and Flp dependent. (C) A Cre/tTA intersectional approach, in which the tTA driver line uses gene-specific promoter 1, and the Cre driver line uses genespecific promoter 2. The double reporter uses the TRE promoter and is also Cre dependent. HZ - 23