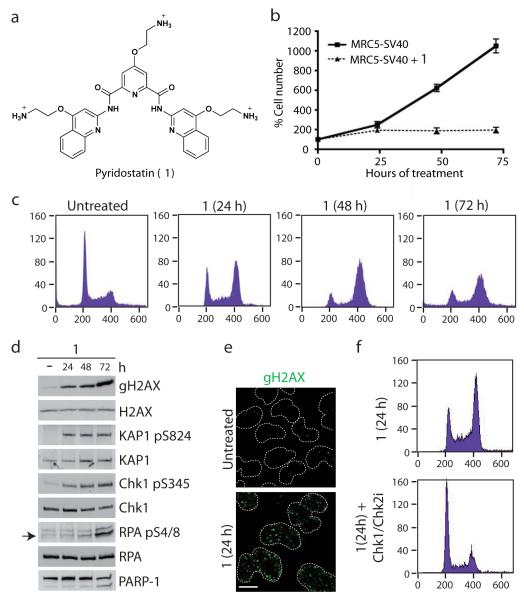
Figure 1. Pyridostatin-induced DNA damage and checkpoint-dependent cell cycle arrest.
(a) Molecular structure of 1; trifluoromethanesulfonate counter anions are omitted for clarity. (b) 1 inhibited cell proliferation (N=3; error bars represent S.E.M.). (c) 1 caused cell accumulation in G2; cells were analyzed by FACS with cell count (y-axis) and DNA content (x-axis) as indicated. (d) 1 activated DDR signalling; western blots were performed with the indicated antibodies. Full gel images are displayed in Supplementary Fig. 2. (e) γH2AX foci induced by 1; cells were treated and analyzed by immunofluorescence (IF); dotted white lines indicate nuclear peripheries. (f) G2/M checkpoint-dependent arrest induced by 1; cells were analyzed as in Fig. 1c 2h after addition of Chk1/Chk2i. MRC5-SV40 cells were used throughout all Figures and were either untreated or treated with 2 μM 1 during 24 h unless otherwise stated. Scale bar, 10 μm.