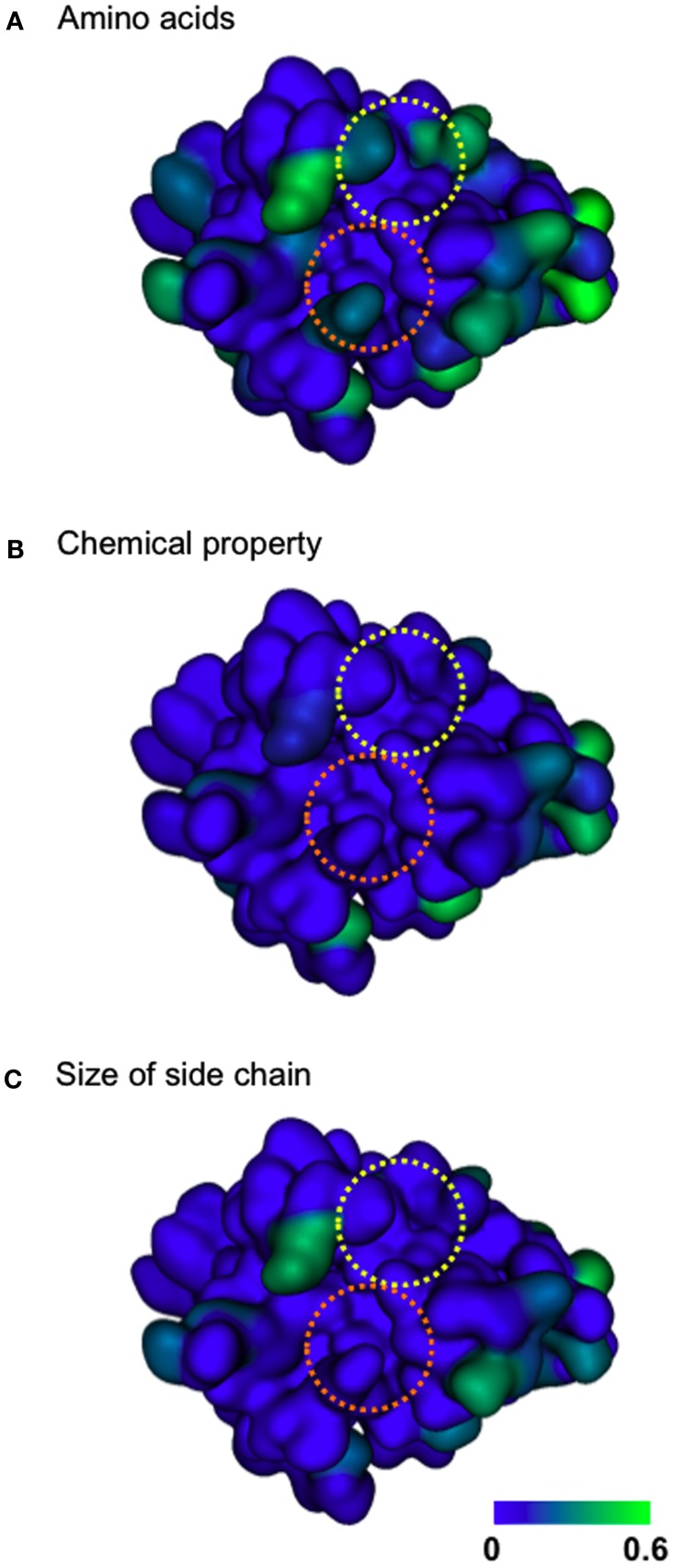
Figure 3.
Diversity of SaV protease amino acid residues. The amino acid diversity at individual sites of the SaV protease domain was analyzed with information entropy as described previously (Oka et al., 2009). The Shannon entropy H was calculated with Shannon’s formula (Shannon, 1948) based on amino acid residues (A), chemical properties (B), and the size of the side chain (C) using amino acid sequences of the SaV full-length protease domain from GenBank (N = 19). For analysis of the diversity in the chemical properties, the amino acid residues were classified into seven groups: acidic (D,E), basic (R,K,H), neutral hydrophilic (S, T, N, Q), aliphatic (G, A, V, I, L, M), aromatic (F, Y, W), thio-containing (C), and imine (P). For analysis of the diversity in the size of the side chain, the amino acid residues were classified into 4 groups: small (G, A, C, S), medium-small (T, V, N, D, I, L, P, M), medium-large (Q, E, R, K), and large (H, F, Y, W). The H scores are plotted on the 3-D structure of the SaV protease model, where an H score of zero indicates absolute conservation. Yellow and orange dotted circles indicate clefts 1 and 2, respectively.