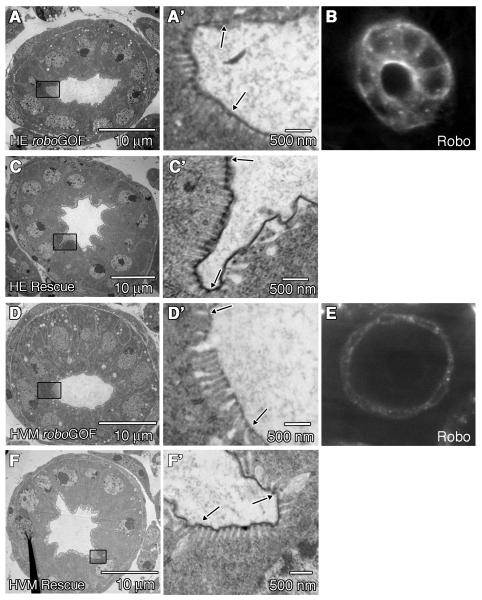
Figure 6.
Robo is required in the HVM for correct microvilli length. (A,C,D,F) are TEM sections through the LI of stage 16 embryos, and (A’,C’,D’,F’) are zoomed in areas of the apical surface of the BCs (outlined by boxes in (A,C,D,F). Arrows indicate borders of the BC. (A,A’) UAS-robo/byn-GAL4 embryo, in which robo is overexpressed in the HE. Microvillus lengths and lumen shape are not significantly affected. (B) Anti-Robo staining in a UAS-robo/byn-GAL4 embryo shown in cross section. As expected, high levels of Robo staining can be seen in the cells of the HE. (C,C’) UAS-robo; roboz570/roboz570;byn-GAL4/+ embryo. Expression of robo in the HE of robo mutant embryos does not rescue lumen shape or microvilli length (P<0.0001 when comparing microvillus lengths between embryos expressing robo only in the HE, and wild type.) (D,D’) UAS-robo/Mef2-GAL4 embryo, in which robo is overexpressed in the HVM. Lumen shape is not affected (D) but the microvilli are significantly longer than wild type (P<0.0001 when comparing microvillus lengths in embryos where robo is overexpressed in the HVM, and wild type) (D’). (E) Anti-Robo staining in a UAS-robo/Mef2-GAL4 embryo. As expected, high levels of Robo staining can be seen in the cells of the HVM. (F,F’) UAS-robo;roboz570/roboz570;Mef2-GAL4/+ embryo. Expression of robo in the HVM in a robo mutant rescues microvilli length (F’) but does not rescue lumen shape (F).