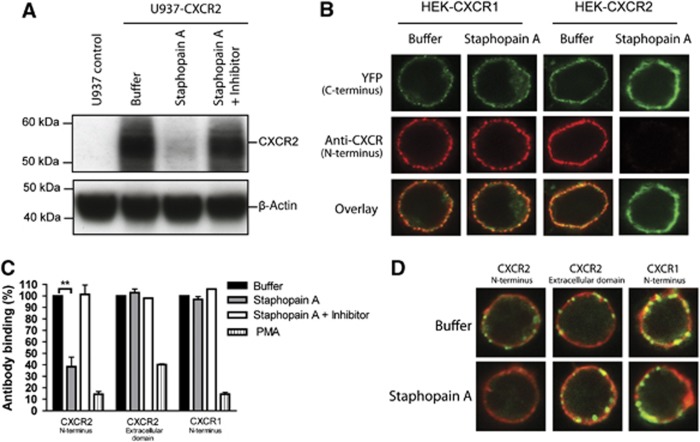
Figure 5.
Staphopain A specifically cleaves the N-terminus of CXCR2. (A) Western blot analysis of U937-CXCR2 cells incubated with buffer, 0.5 μM Staphopain A, 0.5 μM Staphopain A plus 1 μM Staphostatin A for 15 min at 37°C. Whole-cell lysates were analysed by western blotting using an mAb against the N-terminus of CXCR2. Figure represents three independent experiments. (B) Confocal images of HEK cells transfected with human CXCR1 or CXCR2 fused to a C-terminal YFP tag. Cells were incubated with buffer or 0.5 μM Staphopain A for 30 min at 37°C. The N-termini were stained with mAbs and subsequent Alexa633-labelled anti-mouse antibodies. YFP was artificially coloured green. Images are representatives of three independent experiments. (C) Flow cytometry analysis of human neutrophils treated with 0.5 μM Staphopain A or 40 nM PMA for 15 min at 37°C. Cells were first stained with antibodies against the N-terminus of CXCR2, the extracellular loop of CXCR2 or the N-terminus of CXCR1 and subsequently with FITC-labelled secondary antibodies. Antibody binding is expressed in percentages, calculated by dividing the fluorescence of treated cells by fluorescence of buffer-treated cells and multiplying with 100. Figure represents the mean±s.e. of three separate experiments using different donors. **P<0.01 versus buffer (two-tailed Student’s t-test). (D) Confocal images of human neutrophils stained with antibodies against CXCR2 and CXCR1 (green). Cells were treated as described above for (C) after which the membranes were stained with Did (red). Images are representative for three independent experiments using different donors.