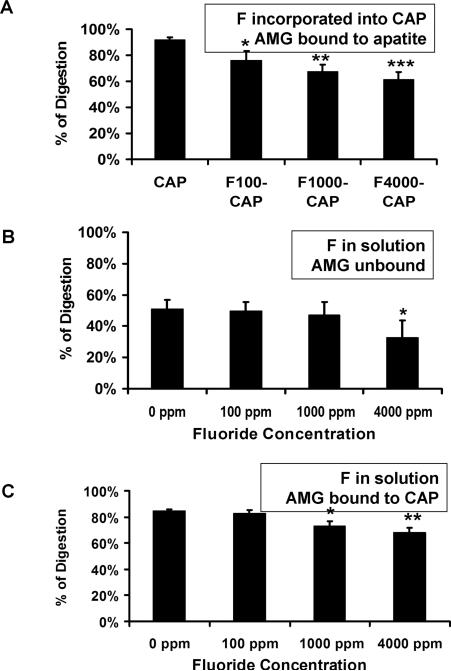
Fig. 2.
The relative percent of amelogenin (AMG) digested by KLK-4. A) KLK4 hydrolysis of AMG bound to apatite decreased relative to increasing amounts of fluoride incorporated into the apatite, with a significant effect even at 100 ppm F B) Fluoride in solution altered KLK4 hydrolysis of AMG only at 4000 ppm F.C) 1000 ppm F in solution significantly inhibitied KLK4 digestion of CAP bound AMG. CAP, carbonated hydroxyapatite; F, fluoride; F100-CAP, F1000-CAP, and F4000- CAP, fluoride-containing carbonated hydroxyapatite (F-CAP) synthesized to contain 100, 1,000, or 4,000 ppm fluoride, respectively. The p-value was derived from a paired t-test. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001.