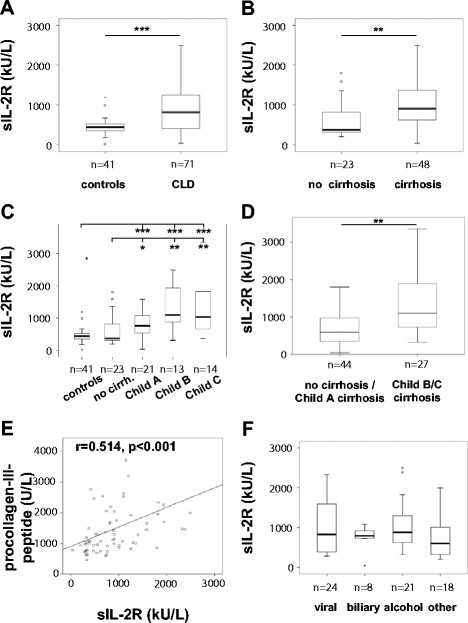
Figure 1.
sIL-2R levels increase in patients with chronic liver disease and are associated with disease progression. Box plots display serum levels of sIL-2R in kU/L for healthy controls versus patients with chronic liver diseases (A), patients without cirrhosis versus cirrhotic patients (B), study participants according to Child-Pugh score (C), and mild versus advanced CLD (D). (E) Levels of sIL-2R correlate with procollagen-III-peptide (r = 0.514, p < 0.001, Spearman rank correlation test). (F) Serum sIL-2R concentrations do not differ among various etiologies of CLD. Significant differences (Kruskal-Wallis and U-test) are marked by *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Open circles and asterixes at the whiskers indicate outlier values.