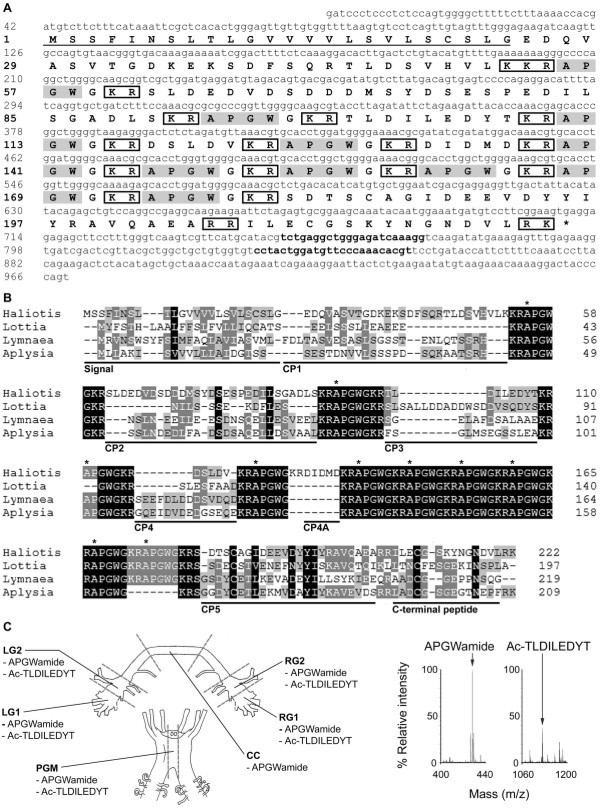
Figure 1.
Characterisation of Has-APGWamide . (A) Nucleotide and predicted amino acid sequence of Has-APGWamide (nucleotide and amino acids are numbered on left). A predicted signal sequence is underlined, and predicted dibasic and tribasic cleavage site residues are boxed. The Has-APGWamide qPCR primers correspond to the nucleotides 750–771 and 830–853, identified here in bold. (B) Multiple sequence alignment of molluscan APGWamide prepropeptide sequences. Shading to four levels shows conservation as per Nicholas et al. (1997) [33]. The start of each H. asinina APGWamide is indicated with an asterisk. HaliotisH. asinina [GenBank:JN606061]; LottiaLottia gigantea[34]; LymnaeaLymnaea stagnalis ([GenBank:1811269A], [35]); AplysiaA. californica ([GenBank: NP_001191561], [30]). (C) Schematic representation of H. asinina anterior ganglia showing regions analysed by MALDI-TOF-MS. Representative mass peaks were identified that match APGWamide (m/z 428.9) and the acetylated CP3 peptide Ac-TLDILEDYT (m/z 1124.8) (right). Signal, signal sequence; LG1, left cerebral ganglia region 1; LG2, left cerebral ganglia 2; RG1, right cerebral ganglia 1; RG2, right cerebral ganglia 2; CC, cerebral commissure; PGM, pleuropedal ganglia middle; Ac, acetylation; amide, amidation; m/z, mass to charge ratio.