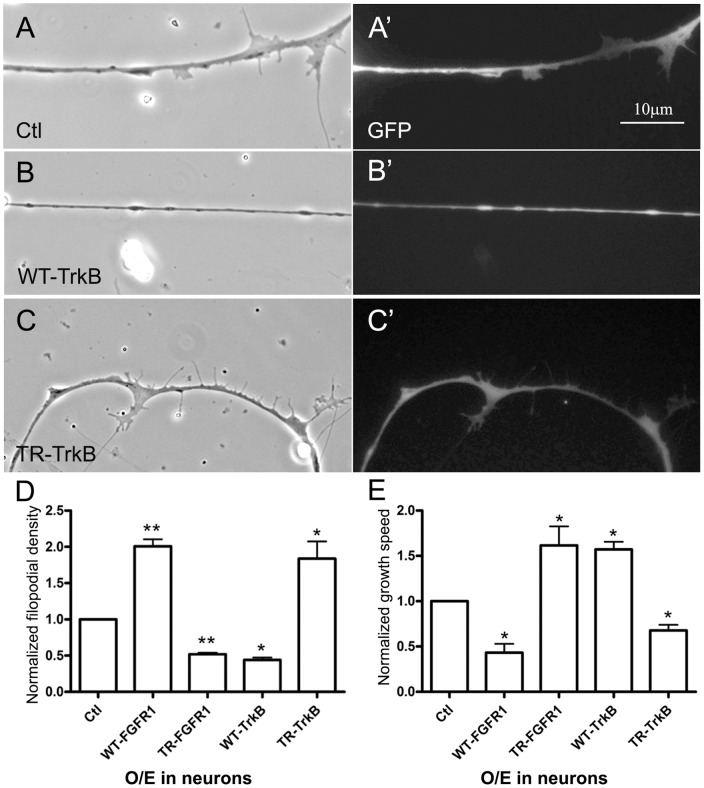
Figure 5. Differential control of filopodial assembly and axonal growth by neuronal FGFR1 and TrkB signaling.
Compared to control (GFP) neurons (A and A'), WT-TrkB-neurons grew fewer filopodia (B and B') and TR-TrkB-neurons grew more filopodia (C and C'); panels A–C and A'–C' show corresponding phase-contrast and GFP images. In panel D the filopodial densities calculated for these neurons are normalized relative to the density in GFP-neurons and are compared to those obtained for neurons expressing active and inactive FGFR1 proteins (Figure 4). E. Axonal growth speeds of neurons expressing FGFR1 or TrkB proteins were measured by time-lapse imaging and normalized relative to the growth of GFP-neurons. Overexpression of WT-FGFR1 or TR-TrkB slowed axonal growth, whereas expression of TR-FGFR1 or WT-TrkB sped it up. Mean and SEM shown; t test: *p<0.05, compared with Ctl.