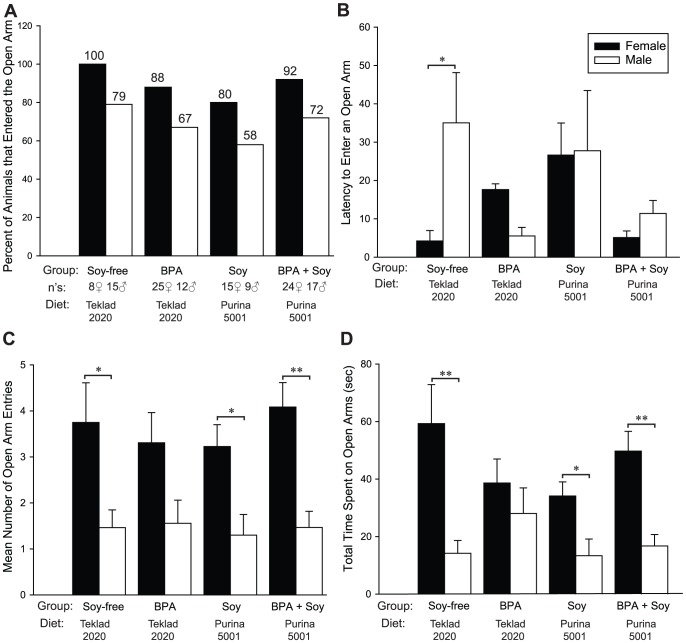
Figure 4. BPA, EE and dietary effects on adult Elevated Plus Maze (EPM) activity.
As expected, a significant gender effect was found for all measurements except latency to enter an open arm. In general, BPA exposure eliminated these sex differences. (A) A higher percent of females entered the open arms than males regardless of exposure group. (B) Soy-free males took significantly longer to enter an open arm than females maintained on the same diet. BPA exposure eliminated this sex difference, with a tendency for reversal. Soy diet also eliminated this behavioral sex difference. (C) Females made significantly more open arm entries than males in all groups except those on the soy-free diet and exposed to BPA (BPA). There was no overall effect of BPA or diet on this behavior. (D) Similarly, in all groups except those on the soy-free diet and exposed to BPA, females spent significantly more time on the open arms than males. Graphs depict mean ± SEM, *P≤0.05, ** P≤0.001.