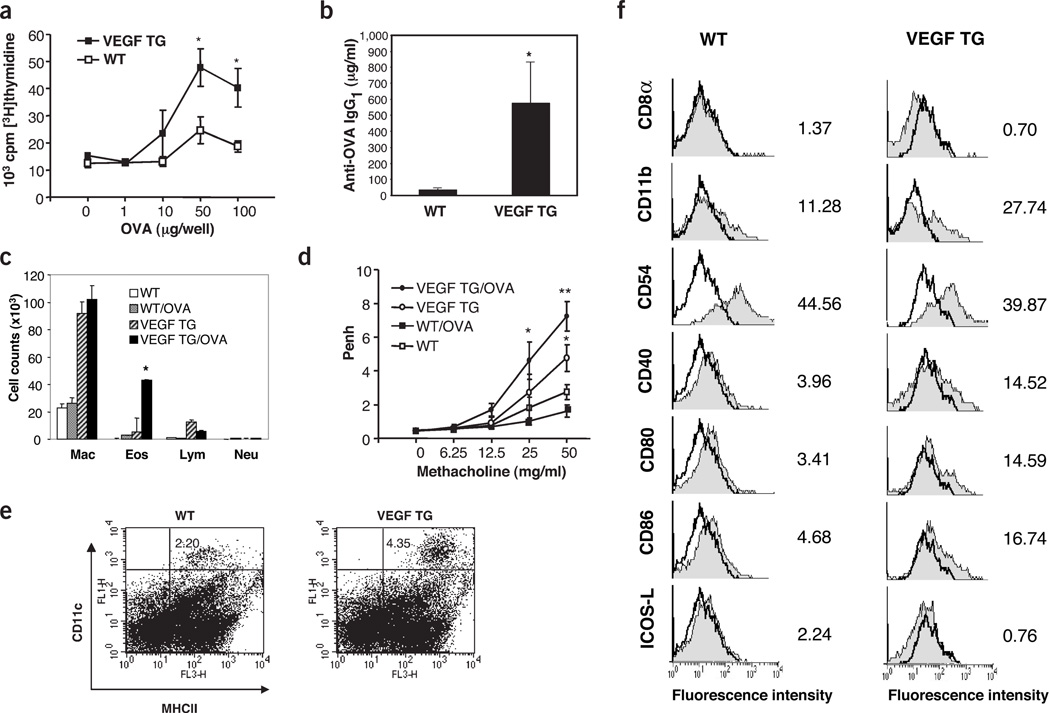
Figure 4.
Immune effects of VEGF. Effect of intranasal OVA in wild-type (WT) and transgenic (TG) mice treated with dox for 2 weeks. (a,b) OVA-induced spleen cell proliferation (a) and OVA-specific IgG1 (b) were assessed (*P < 0.01). (c,d) Dox-treated WT and TG mice were challenged with intranasal OVA, re-challenged after 7 d and, 48 h later, BAL cellularity (c) and AHR (d) were evaluated. (In c, *P < 0.001 versus eosinophils in other groups; in d, *P < 0.01 versus WT and **P < 0.05 versus TG mouse challenged with vehicle.) (e,f) FACS analysis of lung cells isolated from WT mice and TG mice given dox for 7 d and stained with antibodies directed against CD11c, MHC II and with other antibodies as indicated. In f: Cells were sorted for CD11c. CD11c+ cells were incubated with test antibodies (gray) and control antibodies (transparent).