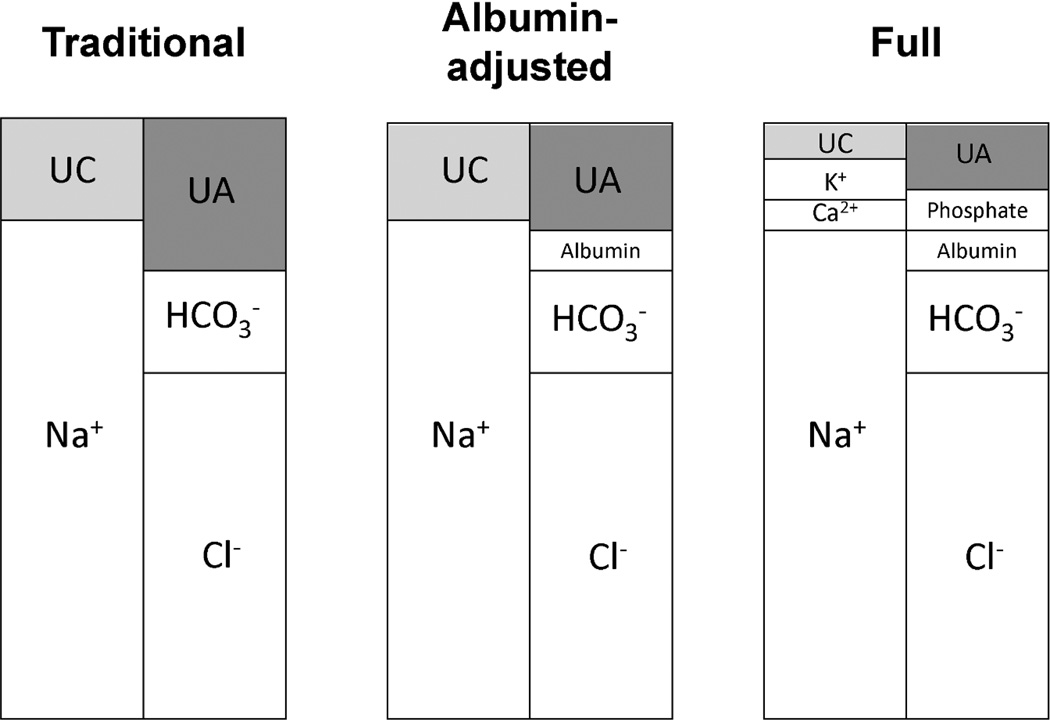
Figure 1.
Graphical depiction of components of the anion gap (AG) in each version of the calculation. Anion gap = Unmeasured anions (UA) – Unmeasured cations (UC). UA and UC are determined by the anions and cations that are accounted for in the calculation. Each panel depicts the components included in each AG calculation. The following definitions were used: Traditional AG=serum sodium(mEq/L) − (serum chloride(mEq/L) + serum bicarbonate(mEq/L)); Albumin-adjusted AG=Traditional AG − (2.5 × serum albumin(g/dL)); Full AG=Albumin-adjusted AG + serum potassium(mEq/L) + ionized calcium(mEq/L) − serum phosphate(mEq/L). The traditional AG calculation includes only Na+, Cl−, and HCO3−. As additional anions and cations are accounted for in the calculation of the albumin-adjusted and full AG, the unmeasured components (UA and UC) become smaller.