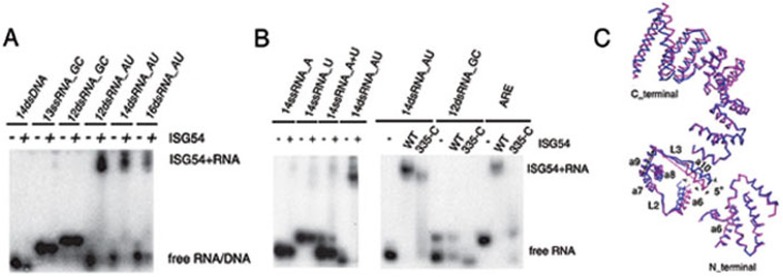
Figure 5.
The RNA-binding specificity of ISG54. (A) EMSA results of ISG54 binding with synthetic model RNAs (sequences shown in Supplementary information, Table S1). ISG54 binds to Poly (AU) but not to GC-rich RNAs and poly (AT). (B) ISG54 cannot bind to 14ssRNA_A, 14ss RNA_U, or the annealed 14ssRNA_A+U (left panel). ISG54 binds to the ARE sequence, using a 14dsRNA_AU as a positive control and 12dsRNA_GC as a negative control (right panel). RNAs alone are shown in lanes 1, 4 and 7. Wild-type ISG54 (lanes 2, 5 and 8) and mutant 335-C (lanes 3, 6 and 9) were pre-incubated with poly (AU), 12dsRNA_GC and ARE, respectively. The RNA-binding ability of truncation mutant 335-C with both 14dsRNA_AU and ARE (lanes 3 and 9) was destroyed. (C) Flexibility of ISG54 structures. Superimposition of the N_terminus (residues 31-91), domain-swapped regions (residues 136-187) and C_terminus (residues 194-334) of monomers A (purple) and B (blue) in the ISG54 dimer. The superimposition was performed using the helix 7-9 bundle as a basis and shows an angle between the two monomers at both helices 6 and 10, which alters the positions of the N- and C-terminus. The superimposition was performed with COOT46 and the angles were measured with PyMOL (http://www.pymol.org/).