Fig 1.
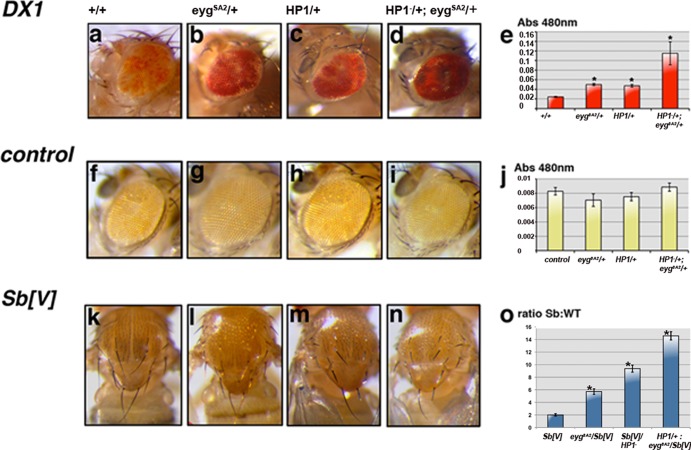
Eyg is required for heterochromatic gene silencing. Effects of mutations in eyg and Su(var)205 on the white+ variegation induced by DX1 transgene repeats (a to e) or a control transgene (f to j), are shown as changes in red eye pigmentation. Altering the dosage of eyg (b) or HP1a (c) suppresses variegation in DX1 flies. Note the increased red eye pigmentation in DX1 flies (d) heterozygous for both eyg and Su(var)205 genes. (e and j) Changes in pigmentation were determined by measuring absorbance at a wavelength of 480 nm. The data are expressed as means ± standard errors of the mean (SEM) (*, P < 0.001 compared with +/+ control; Student's t test; n = 60 per group). control is a single P[white+] element inserted in a euchromatic region that does not induce heterochromatin formation. (k to o) Variegation of Sb in a T(2;3)Sb[V] rearranged chromosome (7) is suppressed by partial depletion of Eyg and/or HP1a. (o) Suppression of Sb variegation is shown as changes in the Sb-to-WT macrochete ratio. The data are expressed as means ± SEM (*, P < 0.005 compared with an Sb[V] control; Student's t test; n = 40 per group).