Fig 3.
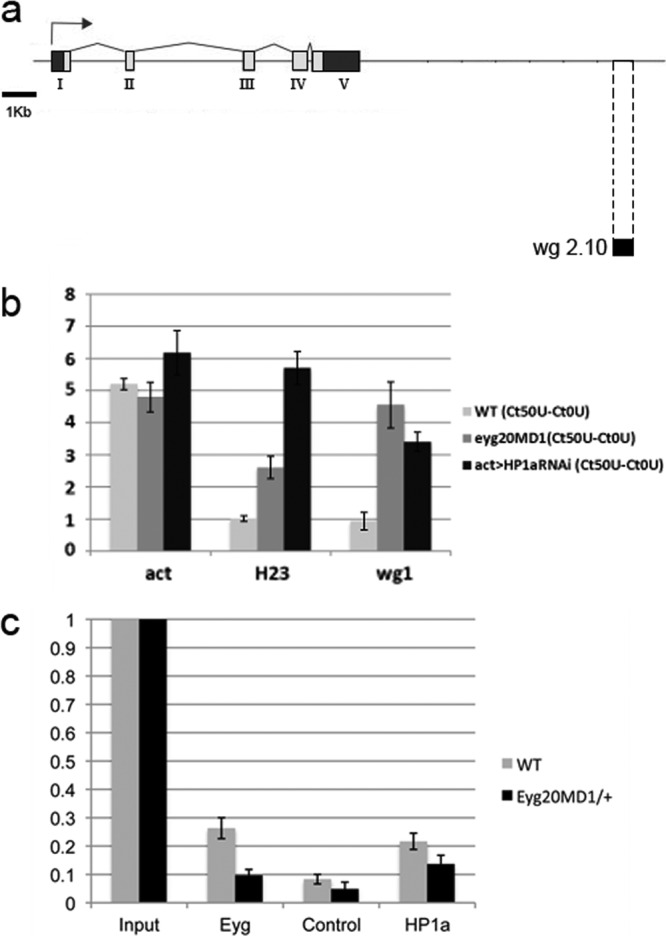
Eyg recruits HP1a and mediates the assembly of a heterochromatic-like structure in the wg enhancer region. (a) Schematic view of the wg genomic region. The wg enhancer region that drives Wg expression in the eye imaginal disc is located at the 3′ end of the genomic region (wg 2.10, black bar). (b) Formation of a DNase I-resistant structure in the wg enhancer region. The act5c and H23 loci were used as controls for open and closed genomic regions, respectively. The bars represent changes in CT values (ΔCT) in the wg enhancer region of wild-type, eyg20MD1/+, and HP1a mutant act>HP1aRNAi eye-antennal disc extracts after treatment with 50 U DNase I. In eyg20MD1/+ heterozygous discs, as well as in act>HP1aRNAi, the wg enhancer region became almost as sensitive to DNase I as the euchromatic actin locus. The H23 locus remained mostly closed for wild-type control and eyg20MD1/+ and open and DNase I sensitive for HP1 mutant extracts. (c) Analysis of HP1a and Eyg binding to the wg enhancer region using ChIP. A similar enrichment in binding to the wg enhancer region was found in wild-type control chromatin immunoprecipitated with an anti-Eyg or an anti-HP1a antibody. Binding of Eyg and, to some extent, HP1a was reduced in the chromatin of eyg20MD1/+ eye-antennal disc extracts.
