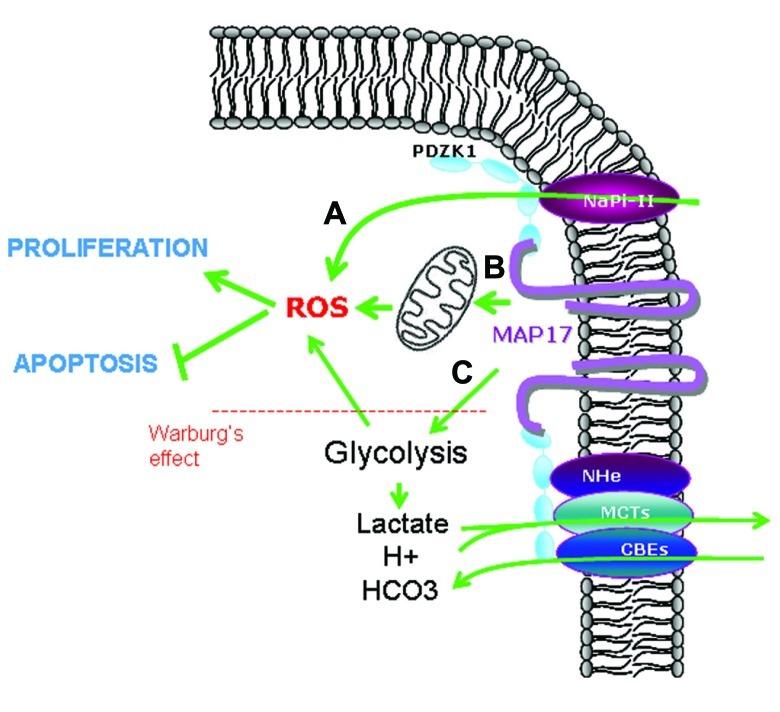
FIGURE 4.
Possible mechanisms involved in MAP17-dependent increase of ROS. (A) Direct pH alteration by membrane transports, (B) increase in glucose metabolism through mitochondrial respiration, (C) increase in aerobic glycolysis (Warburg’s effect) which is allowed by acidic detoxification carried out by membrane transports bund to MAP17–NHeRFs complexes.