Fig 1.
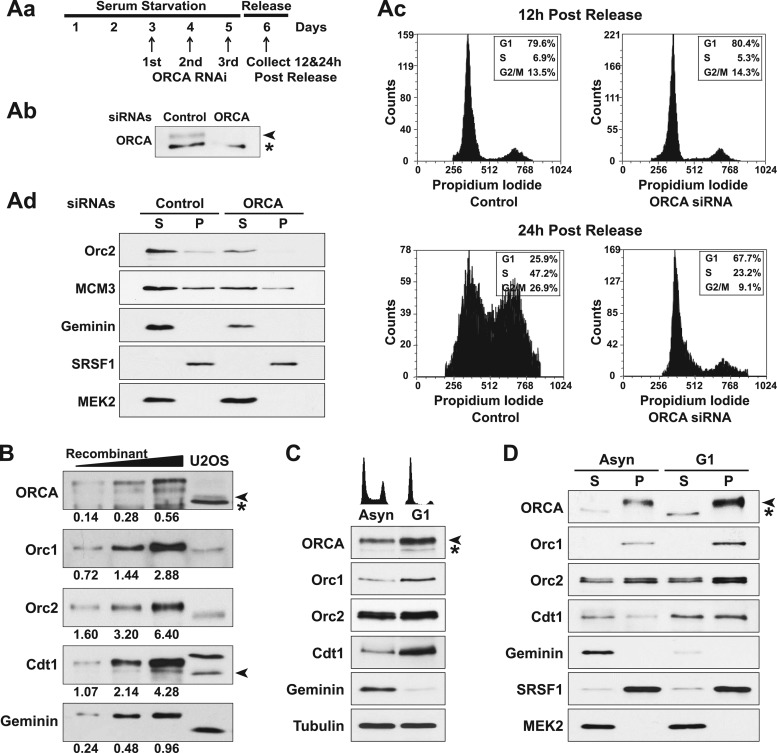
ORCA is required for entry into the cell cycle. (Aa) Scheme of the experiment in WI38 cells. Cells were serum starved for 5 days. ORCA or control siRNA was transfected three times at intervals of 24 h starting day 3. On day 6, the cells were released from arrest for fluorescence-activated cell sorter (FACS) or immunoblot analysis. (Ab) Immunoblot showing efficient knockdown of ORCA. (Ac) FACS analysis at 12 h and 24 h postrelease in control and ORCA siRNA-treated cells. Note the efficient release of cells into the cell cycle in the 24-h FACS profile for control cells but a G1 arrest in ORCA-depleted cells. (Ad) Chromatin fractionation in control and ORCA siRNA-treated cells and immunoblotting with Orc2, MCM3, and geminin. SRSF1 and MEK2 are shown as loading controls for chromatin (P) and cytosolic (S) fractions, respectively. (B) Relative levels of ORCA, Orc1, Orc2, Cdt1, and geminin in asynchronously growing human U2OS cells. GST-tagged ORCA and His-tagged Orc1, Orc2, Cdt1, and geminin were loaded as indicated (ng) for quantitation. (C) Relative levels of ORCA, Orc1, Orc2, Cdt1, and geminin in the G1 phase of U2OS cells. Note that ORCA, Orc1, and Cdt1 levels are high during G1, whereas geminin levels are negligible in G1. Asyn, asynchronous. (D) Relative abundances of ORCA, Orc1, Orc2, Cdt1, and geminin on chromatin (P) during G1 in human U2OS cells. The asterisks indicate cross-reacting bands. The arrowheads indicate endogenous ORCA (ORCA immunoblot) and endogenous Cdt1 (Cdt1 immunoblot).