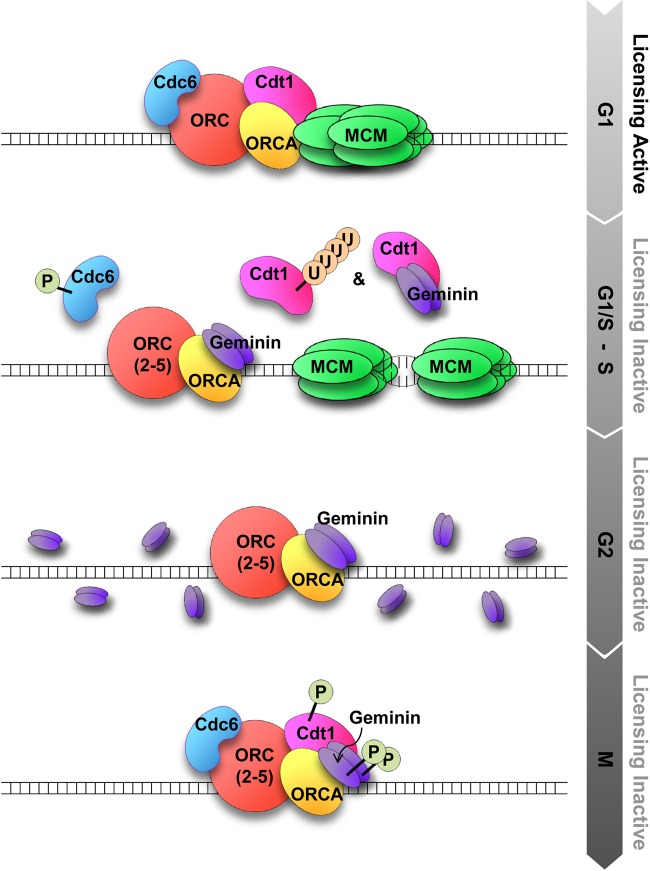
Fig 8.
Model depicting ORCA association with the pre-RC components in a cell cycle-regulated manner. In late M/G1, ORCA associates with ORC and Cdt1. Along with Cdc6, pre-RCs are assembled at origins. ORCA is abundant in the G1 phase. One prediction would be that ORCA acts as a scaffold and facilitates the assembly of Cdt1 during M and G1 and that of geminin at the end of G1 on the chromatin. At the end of G1, geminin levels begin to rise. The balance in the Cdt1-geminin ratio at this time point favors replication licensing. At the G1/S boundary, as geminin levels begin to increase significantly and ORCA levels begin to decrease, ORCA-Cdt1 interaction is lost and geminin titrates all the Cdt1 away from ORCA, and hence from the origins. This makes the complex licensing inactive, following which Cdt1 is ubiquitinated and degraded. During G2, the ORCA-ORC(2-5)-geminin complex prevents licensing. During mitosis, an ORCA-ORC(2-5)-phosphorylated Cdt1-phosphorylated geminin complex exists, and at the end of mitosis, geminin is degraded and Orc1 is dephosphorylated, and thus, a functional pre-RC is assembled.