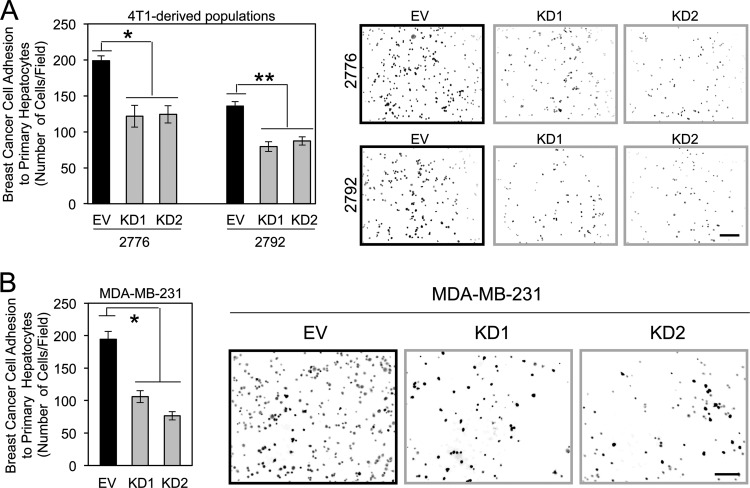
Fig 5.
Claudin-2 functions to promote breast cancer adhesion to hepatocytes. (A) The indicated breast cancer cells were plated onto primary hepatocyte monolayers, and adhesion was quantified after 1 h. Liver-aggressive cells infected with two independent Cldn2 shRNA expression vectors (knockdown [KD1 and KD2]) or harboring the empty vector (EV) were analyzed. Diminished claudin-2 levels in liver-aggressive cells (KD1 and KD2) resulted in statistically significant decreases in hepatocyte adhesion compared to control cells (empty vector) (∗, P = 0.016; ∗∗, P = 0.033). Representative images of each cell population following adhesion to a monolayer of primary hepatocytes are shown. The scale bar (bottom right) represents 200 μm. (B) Human MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells were infected with two independent human Cldn2 shRNA expression vectors (KD1 and KD2) or an empty vector and analyzed for their abilities to adhere to primary hepatocyte monolayers. Diminished claudin-2 levels in MDA-MB-231 cells (KD1 and KD2) resulted in statistically significant decreases in hepatocyte adhesion compared to control cells (empty vector) (∗, P = 0.015). Shown are representative images of each cell population following adhesion to a monolayer of primary hepatocytes. The scale bar (right) represents 200 μm.