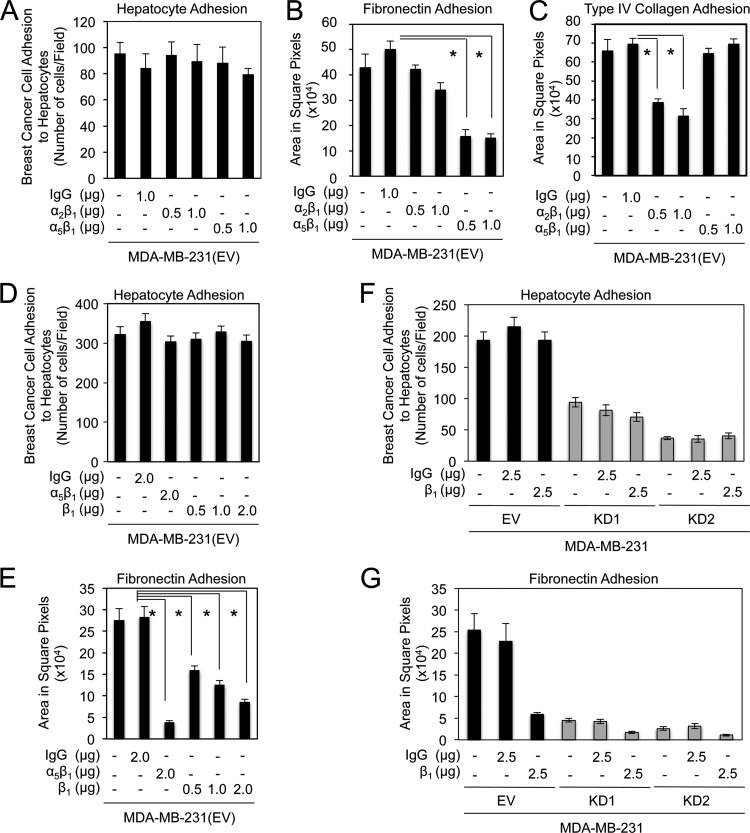
Fig 6.
β1-containing integrins do not participate in claudin-2-mediated breast cancer cell adhesion to hepatocytes. (A to C) The numbers of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells that adhered to a monolayer of primary hepatocytes (A), fibronectin (B), or type IV collagen (C) following incubation with a control isotype or increasing concentrations of blocking antibodies against α2β1- and α5β1-integrin complexes were quantified. Blocking antibodies against α2β1- and α5β1-integrin complexes effectively prevented adhesion to collagen type IV and fibronectin, respectively. These antibodies failed to impair MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell adhesion to primary hepatocytes. (D and E) The number of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells that adhered to a monolayer of primary hepatocytes (D) or fibronectin (E) following incubation with a control isotype or increasing concentrations of blocking antibodies against integrin-β1 were quantified. While blocking antibodies against the integrin-β1 subunit or the α5β1-integrin complex prevented adhesion to fibronectin, they had no effect on breast cancer adhesion to primary hepatocytes (∗, P < 0.001). (F and G) The numbers of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells that possessed normal or diminished claudin-2 expression levels, which adhered to a monolayer of primary hepatocytes (F) or fibronectin (G) following incubation with a control isotype or blocking antibodies against β1-integrin, were quantified. Blocking antibodies against β1-integrin-containing complexes effectively prevented breast cancer cell adhesion to fibronectin, but failed to impair MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell adhesion to primary hepatocytes. For panel F, the P value was < 0.0001 for KD1 or KD2 versus the empty vector with no treatment (∗), KD1 or KD2 versus the empty vector with 2.5 μg IgG isotype control antibody (∗∗), and KD1 or KD2 versus the empty vector with 2.5 μg β1-neutralizing antibody (∗∗∗). For panel G, the P value was <0.0001 (∗).