Fig 8.
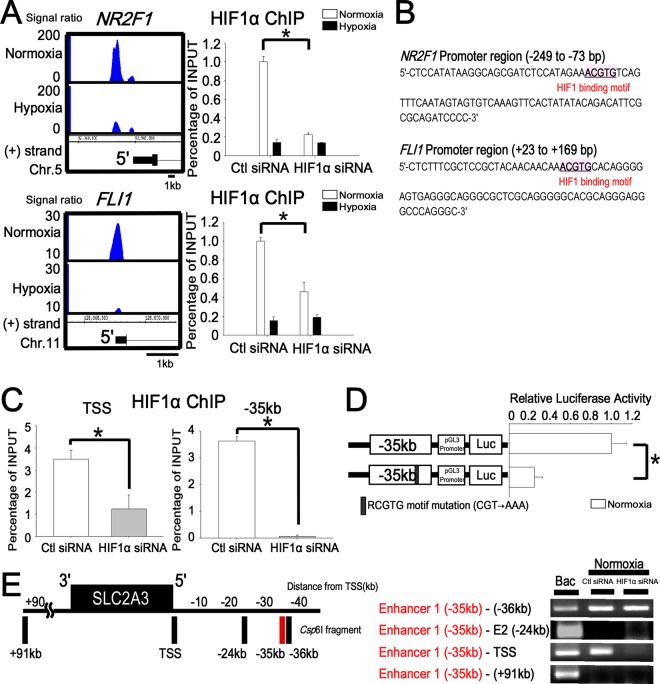
HIF1 binds to the TSS and enhancer 1 (kbp −35) under normoxia and maintains the chromatin conformation. (A) Representative HIF1 binding sites and ChIP-PCR validations under normoxia (NR2F1 and FLI1). The promoter regions of NR2F1 and FLI1 were validated by ChIP-PCR to confirm HIF1 binding under normoxia. When HIF1α was knocked down by siRNA, the enrichment of HIF1 at the TSS of NR2F1 and FLI1 was significantly reduced. *, P < 0.05 compared with control siRNA. The experiments were performed three times independently. (B) HIF1 binding RCGTG motif in the NR2F1 and FLI1 promoters. (C) ChIP-PCR validation of the HIF1 binding sites under normoxia at the SLC2A3 loci. TSS and enhancer 1 (kbp −35) were validated by ChIP-PCR to confirm HIF1 binding under normoxia. When HIF1α was knocked down by siRNA, the enrichment of HIF1 at the TSS and enhancer 1 (kbp −35) was significantly reduced under normoxia. *, P < 0.05. The experiments were performed three times independently. (D) Reporter assay of the SLC2A3 enhancer 1 (kbp −35) in combination with the pGL3-promoter vector under normoxia. Enhancer 1 (kbp −35)-luc and enhancer 1 (kbp −35) with a mutation in motif 4 (mut 4) were transiently transfected into HUVECs and assayed for luciferase activity. *, P < 0.001 compared with the activity from pGL3 promoter-luc under normoxia. The experiments were performed three times independently. (E) Long-range interactions between the SLC2A3 promoter and enhancer as measured with 3C-ChIP. The vertical black bars represent each Csp6I fragment at target sites. The numbers depict the distance (in kbp) from the TSS. The 3C-ChIP assay was conducted in HUVECs under normoxia. The interaction of enhancer 1 (kbp −35) and the TSS under normoxia disappeared when HIF1α was knocked down by siRNA. The site at kbp +91 served as a negative control. The experiments were performed three times independently.