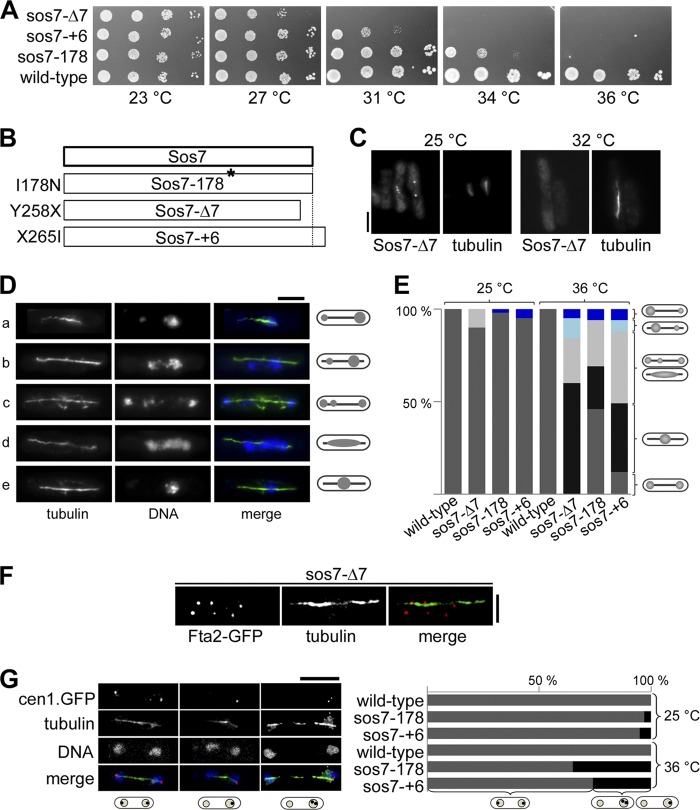
Fig 3.
Sos7 mutant strains have severe mitotic defects. (A) Serial dilution patch tests (104 to 101 cells) of 3 sos7ts mutant strains. The indicated strains were grown at the various temperatures for 3 to 4 days. (B) Amino acid changes found in the Sos7 mutant proteins. (C) Kinetochore localization of Sos7-Δ7 at 25°C and after 6 h at 32°C. Fixed cells were stained with our anti-Sos7 antibody and the TAT-1 antitubulin antibody. Bar, 5 μm. (D) Photomicrographs of sos7ts cells incubated at 36°C for 6 h (a, sos7-+6; b and c, sos7-178; d and e, sos7-Δ7). Fixed cells were stained with antitubulin antibody and DAPI. Shown are all mutant phenotypes (unequally separated chromatin [cells a and b], segregated chromatin with lagging chromosomes [cell c], smeared chromatin [cell d], and nonseparated chromatin [cell e]) on an elongated spindle. (E) Quantification of the phenotypes described for panel D. The number of cells analyzed per strain and temperature was 100. (F) Photomicrographs of a mitotic sos7-Δ7 cell expressing endogenous Fta2-GFP. Cells were incubated at 36°C, fixed, and stained with antitubulin and anti-GFP antibodies. Bar, 2 μm. The number of mitotic Fta2-GFP signals analyzed was 327. (G) (Left) cen1-gfp sos7-178 cells incubated at 36°C for 6 h. Fixed cells were incubated with anti-GFP antibody, DAPI, and antitubulin antibody. Bar, 5 μm. (Right) Quantification of GFP signal distribution in wild-type and sos7ts strains at 25°C and 36°C. The number of cells analyzed per strain and temperature was 100.