Fig 7.
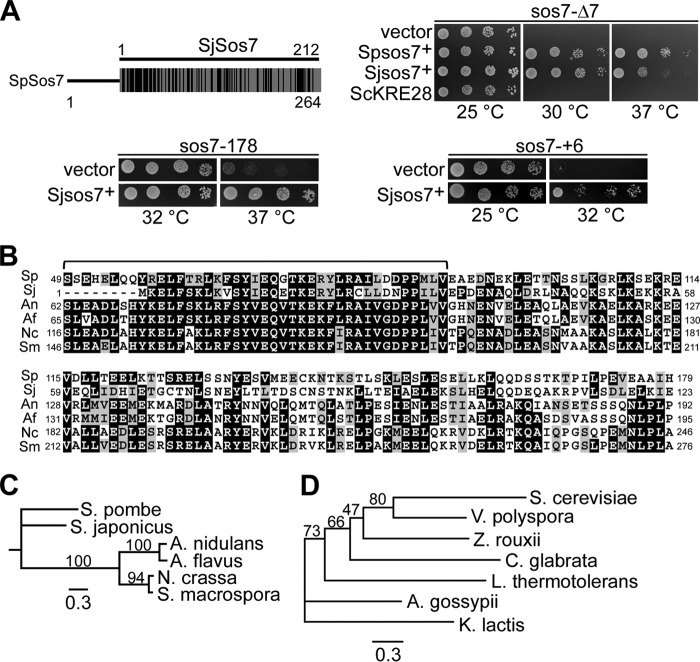
Sos7 belongs to a conserved protein family. (A) Diagrammatic representation of the comparison of Sos7 proteins from S. pombe and S. japonicus. Black bars indicate regions of identity and similarity. Clockwise from top right: serial dilution patch tests (104 to 101 cells) of sos7-Δ7 transformants expressing a vector control, S. pombe Sos7 (Spsos7+), S. japonicus Sos7 (Sjsos7+), or S. cerevisiae Kre28 (ScKRE28); sos7-+6 cells transformed with vector control or a plasmid with Sjsos7+; and sos7-178 cells transformed with vector control or a plasmid with Sjsos7+. (B) Amino acid sequence comparison of Sos7-like proteins from S. pombe, S. japonicus (XP_002174481), Aspergillus nidulans (CBF76747), Aspergillus flavus (XP_002383989), Neurospora crassa (CAE76380), and Sordaria macrospora (XP_003347116). Black boxes, ≥50% identity; gray boxes, ≥50% similarity (http://www.ch.embnet.org/software/BOX_form.html). A bracket indicates a highly conserved sequence motif. (C) Phylogenetic tree of Sos7 homologues shown in panel B. (D) Phylogenetic tree of Kre28 and V. polyspora homolog EDO18951, Z. rouxii CAR29059, A. gossypii AAS54100, C. glabrata XP_446867, L. thermotolerans CAR23808, and K. lactis XP_452234. The trees in panels C and D were engendered by PhyML 3.0 based on the maximum-likelihood method using the Jones Taylor Thornton substitution matrix (18). Bootstrap values (100 replicates) are shown. The scale bar indicates the length of the branch.