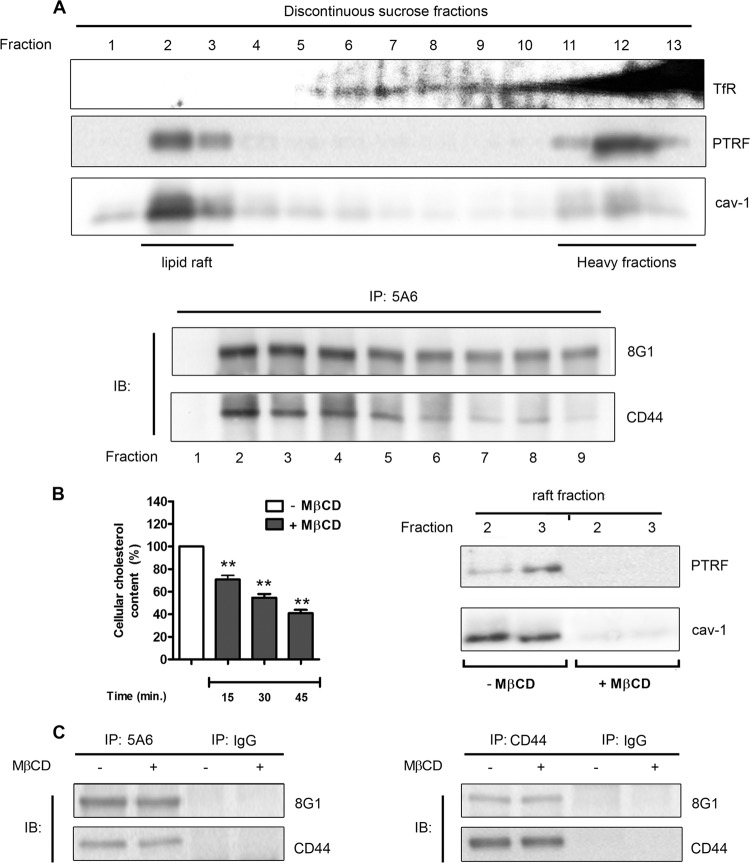
Fig 5.
LRP-1 and CD44 are found associated in both raft and nonraft fractions. (A) In the top panel, FTC-133 cell lysates were subjected to a discontinuous sucrose density gradient ultracentrifugation. PTRF and caveolin 1 (cav-1) were used to reveal raft fractions, whereas the transferrin receptor (TfR) was used as a marker of nonrafts. In the bottom panel, immunoprecipitation assays (IP) were conducted with fractions 1 to 9 by using anti-LRP-1 antibody (5A6) followed by immunoblotting revelation using anti-LRP-1 (8G1) and anti-CD44 (A020) antibodies. The fractions used for immunoprecipitation are indicated under the membrane picture. (B) FTC-133 cells were treated with or without 5 mM methyl-β-cyclodextrin (MβCD). In the left panel, cholesterol content was then quantified at different times of incubation (15, 30, and 45 min). Results were expressed as percentages of results for nontreated cells. In the right panel, after 30 min of incubation with or without MβCD, raft fractions (fractions 2 and 3) were isolated by sucrose density gradient ultracentrifugation, as described above, and checked for PTRF and cav-1 expression by immunoblotting. (C) FTC-133 cells were treated or not with MβCD for 30 min. After biotinylation of cell surface proteins, LRP-1-containing complexes (left panel) or CD44-containing complexes (right panel) were immunoprecipitated by either the anti-LRP-1 β-chain (5A6) or anti-CD44 (F10-44-2), respectively. Immunoblotting analysis (IB) was realized with anti-LRP-1 (8G1) and anti-CD44 (A020) antibodies. Nonspecific IgGs were used as a negative control of immunoprecipitation assays.