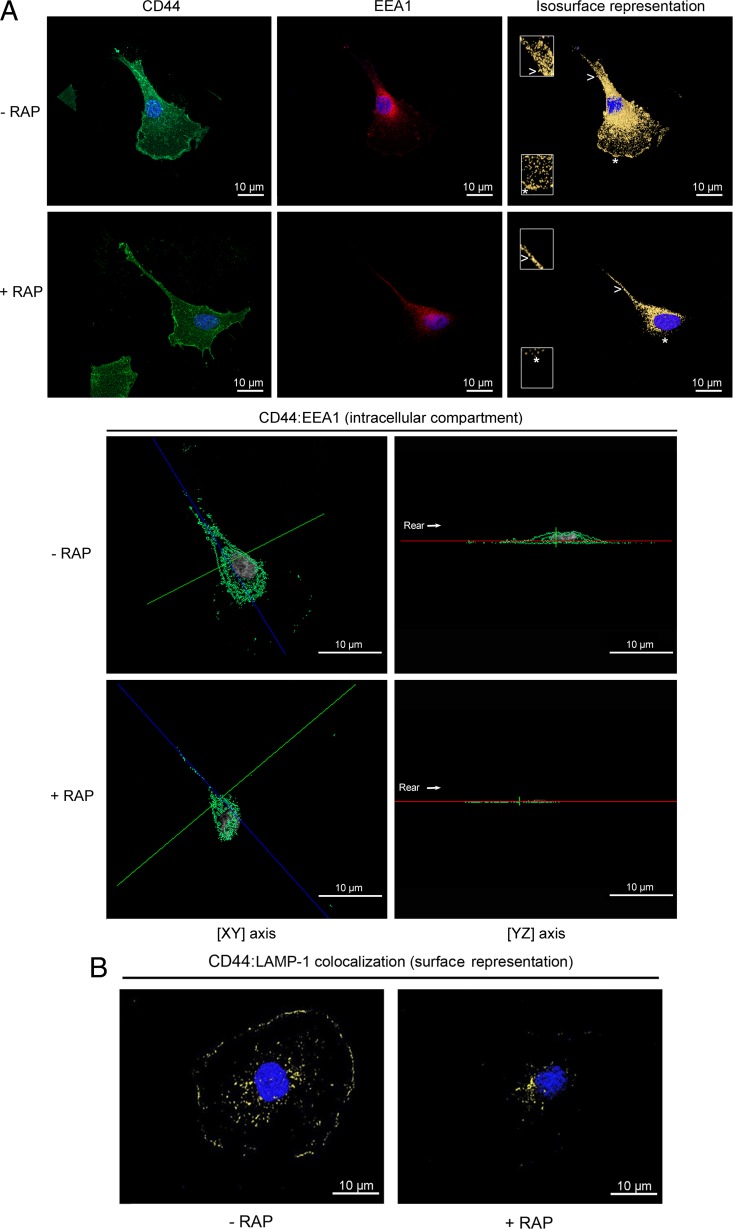
Fig 7.
CD44 colocalization with EEA-1 and LAMP-1 is LRP-1 dependent. FTC-133 cells were plated on gelatin-coated coverslips for 4 h at 37°C and treated or not with 500 nM RAP for 1 h. (A) Cells were stained with Alexa Fluor 488 for CD44 (green) and Alexa Fluor 568 for EEA-1 (red). Nuclei were counterstained in blue with DAPI. Cells were analyzed by confocal microscopy, and images were processed using the AMIRA software program. In the top panel, CD44 labeling (left), EEA-1 labeling (middle), and isosurface representation (right), without RAP (- RAP) or under RAP treatment (+ RAP), are shown. Insets (zoomed in 200%) from the leading edge (star) and the rear of the cell (arrowhead) highlight that colocalization of CD44 with EEA-1 was drastically disturbed by RAP treatment. In the bottom panel, intracellular colocalization of CD44: EEA-1 (green spots) in FTC-133 cells treated without RAP (- RAP) or with RAP (+ RAP), as revealed by one single cross section (xy axis in left; yz axis in right), is shown. The rear of the cell is indicated by the arrow. (B) Cells were treated without RAP (- RAP) or with RAP (+ RAP) and were stained with Alexa Fluor 488 for CD44 (green) and Alexa Fluor 568 for LAMP-1 (red), and an isosurface representation (yellow spots) is displayed. All images are representative of three independent experiments. Bars, 10 μm.