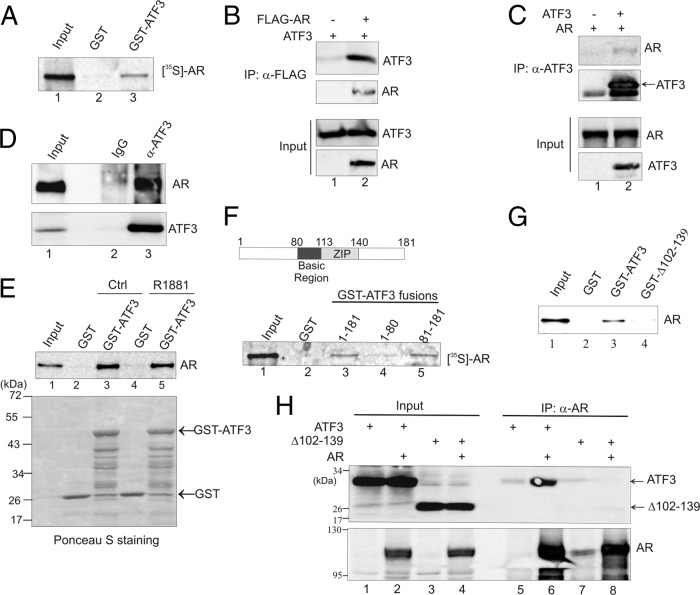
Fig 1.
ATF3 interacts with AR via its ZIP domain. (A) GST-ATF3 or GST was immobilized onto glutathione-agarose and incubated with AR labeled with [35S]methionine by in vitro translation. After extensive washes, bound proteins were eluted and visualized by electrophoresis followed by fluorography. (B) PC3 cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids and then subjected to co-IP using anti-FLAG antibody. Precipitated proteins were detected by Western blotting. (C) AR was coexpressed with or without ATF3 in PC3 cells by transfections. Cell lysates were subjected to co-IP using anti-ATF3 antibody followed by Western blotting. (D) LNCaP cell lysates were incubated with anti-ATF3 antibody or rabbit IgG at 4°C overnight and then precipitated with protein A-agarose. Bound proteins were eluted and subjected to Western blotting. (E) In vitro-translated AR was preincubated with or without 100 nM R1881 for 1 h and then subjected to GST pulldown assays to examine the ATF3-AR interaction. (F) The indicated GST-ATF3 fusions were incubated with 35S-labeled AR and subjected to GST pulldown assays. (G) The full-length ATF3 and a mutant lacking the ZIP domain (Δ102–139) were fused to GST and incubated with in vitro-translated AR for GST pulldown assays. Bound proteins were detected by Western blotting with the anti-AR antibody. (H) ATF3 or ATF3 Δ102–139 was coexpressed with or without AR in PC3 cells and then subjected to co-IP assays with anti-AR antibody, followed by Western blotting. α, anti.