Fig 7.
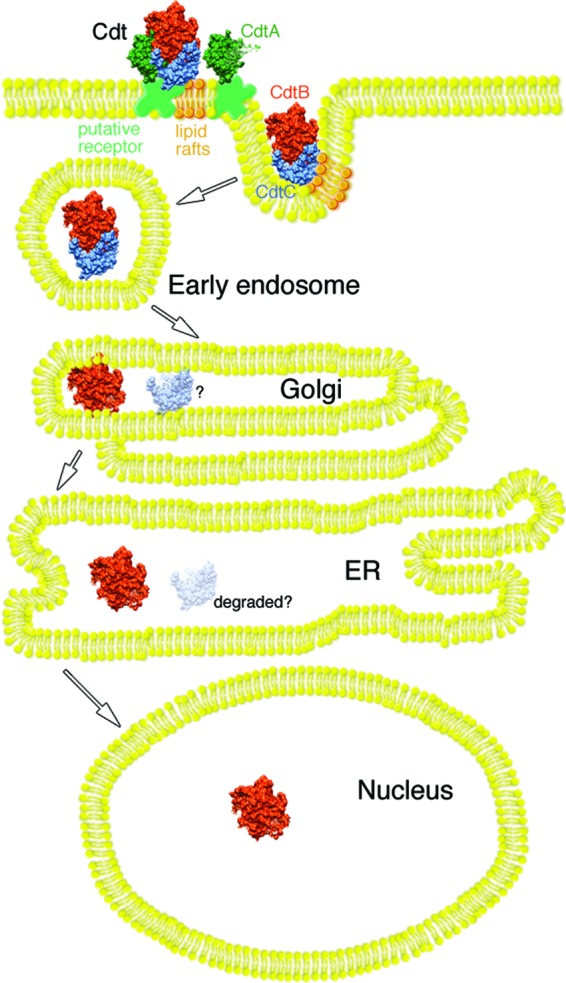
Model of Cdt intoxication of CHO-K1 cells. The CdtA subunit anchors the heterotrimer to a putative specific receptor in the cell membrane, while CdtC plays an accessory role in the binding process. Interaction of the CdtC with lipid rafts, through a cholesterol recognition amino acid consensus (CRAC) domain, enhances the binding and may facilitate enclosure of a CdtB-CdtC dimer in early endosomes. A CdtB-CdtC dimer retrogradely passes to the endoplasmic reticulum from the Golgi apparatus. During this process, CdtC most likely dissociates from the CdtB subunit and is degraded by the ER-associated degradation (ERAD) pathway (depicted by the faded CdtC subunit and the question mark). Evidence suggests that CdtB is subsequently processed through the ER and delivered to the nucleus bypassing the ERAD pathway (12).
