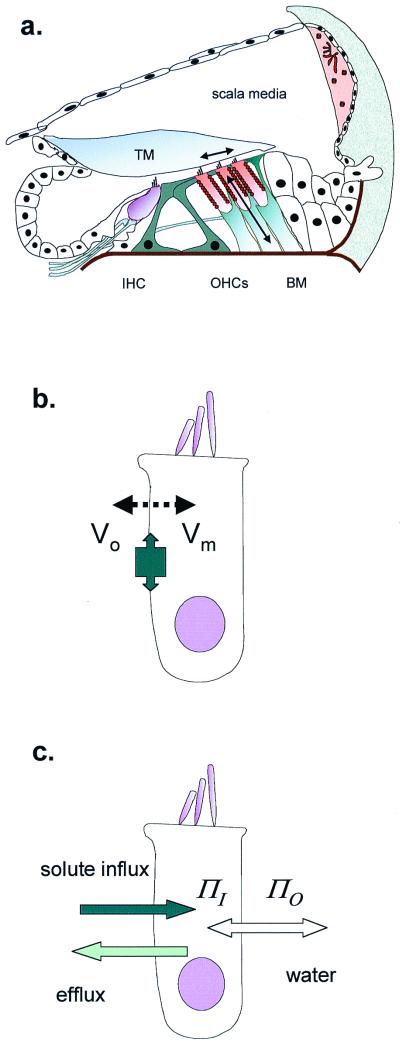
Figure 1.
OHCs in the cochlea. (a) Schematic cross section of the organ of Corti, showing site of inner hair cells (IHC) and OHCs. The primary stimulus is the shear delivered to the OHC stereocilia by the tectorial membrane (TM). OHC length changes (and therefore forces) are produced as arrowed. BM, basilar membrane. (b) OHC length change through electromotility, where membrane potential (Vo − Vm) alters cell surface area. The tight molecular packing in the lateral membrane allows the protein area change to have macroscopic effects. (c) OHC cell length change through cell volume change, where osmotic pressure (ΠO − ΠI) difference inside and outside requires water to follow solute entry.