Figure 1. Histology shows that cortical expression of TDP-43 increases the levels of TDP-43 in motor cortex.
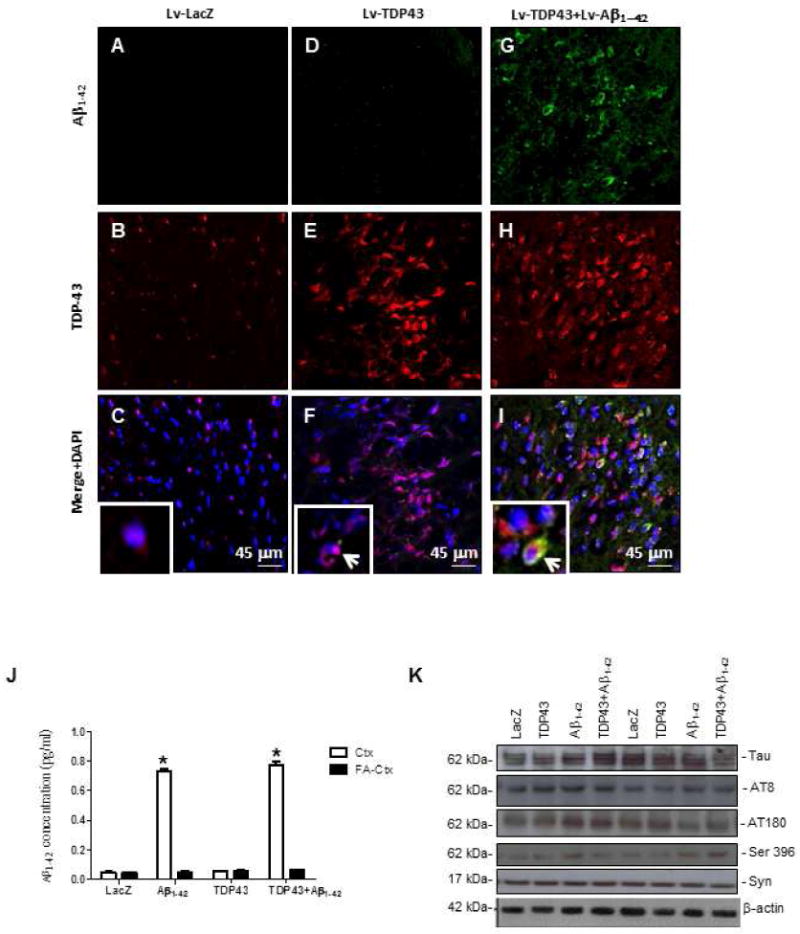
Staining with human-specific Aβ1-42 immunostaining of 20μm-thick sections of rat motor cortex injected with (A) Lv-LacZ, (D), Lv-TDP-43, or (G) Lv-TDP-43+Lv-Aβ1-42. Staining with TDP-43 of 20μm-thick cortical brain sections injected with (B) Lv-LacZ, (E) Lv-TDP-43, or (H) Lv-TDP-43+Lv-Aβ1-42. Co-localization of Aβ1-42 and TDP-43 in 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI)-positive cells in (C) Lv-LacZ, (F) Lv-TDP-43, or (I) Lv-TDP-43+Lv-Aβ1-42. Inserts show higher magnification images of DAPI stained sections to demonstrate cellular TDP-43 localization, arrows indicate cytosolic co-localization of TDP-43 and Aβ1-42 or cytosolic TDP-43 (I). (J) Human specific anti-Aβ1-42 ELISA showing levels in rat brains injected with Lv-LacZ, Lv-TDP-43, Lv-Aβ1-42, or Lv-TDP-43+Lv-Aβ1-42. (K) Western blot analysis of cortical brain lysates probed with total Tau, Tau epitopes (AT8, AT180, Ser 396), and α-Synuclein. N = 8 animals per treatment. Lentiviral lacZ: Lv-LacZ, Lentiviral Aβ1–42: Lv-Aβ1–42, Lentiviral TDP-43: Lv-TDP-43.
