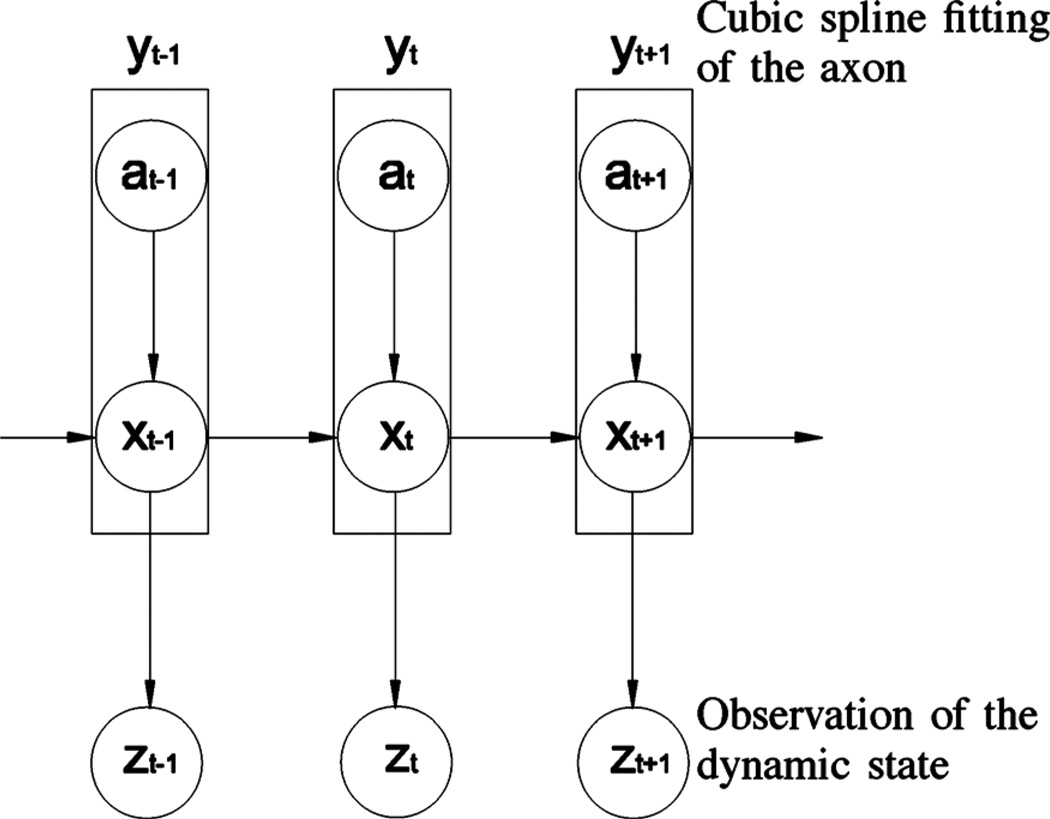
Fig. 2.
Graphical representation of the spatially constrained probabilistic model for neurofilament tracking. x represents the dynamic state, a represents the axon constraint, y represents the compound dynamic state resulting from the combination of a and x, and z represents the observation state. The dynamic state (position, orientation, and velocity) of the moving neurofilament at time t depends on the dynamic state in the prior time interval, t-1, and the constraint imposed on the position and orientation of the neurofilament by the axon at time t.