Fig 1.
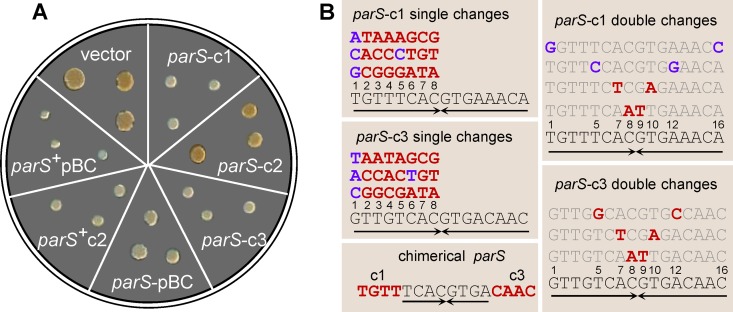
Extra parS sites inhibit growth in B. cenocepacia J2315. (A) Growth inhibition induced by wild-type parS sequences. Each sector shows three colonies of J2315-Mex1 4 days after transformation with the pMMB206 vector or recombinant derivatives carrying parS-c1, -c2, -c3, or -pBC in single copy or the parS-c2 and -pBC clusters (denoted parS+). (B) Mutated parS-c1 and parS-c3 sequences tested for growth inhibition. Each single-base change in parS-c1 and parS-c3 (left top and middle boxes) is shown above its corresponding wild-type base (numbered), in blue when silent (i.e., still growth inhibitory) or in red when leading to loss of function (i.e., allowing normal growth). Doubly mutated parS-c1 and parS-c3 (right boxes) are shown above the wild-type sequence, with changed bases in blue or red as described above. The chimeric parS-c1/c3 sequence, a loss-of-function mutant, is shown (bottom left), with the noncomplementary parS-c1 and parS-c3 ends indicated in red. Arrows, inverted repeated sequences.