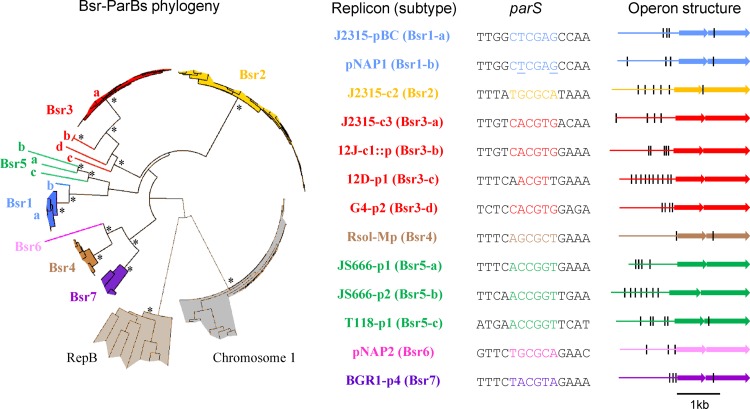
Fig 3.
Bsr families and corresponding parS palindromes. Each color corresponds to one of the seven Bsr families. ParB proteins and loci are listed in Table S1 in the supplemental material. For clarity, only the bootstrap values superior to 800 concerning the deep branches are indicated (*). RepB proteins from Rhizobiales megaplasmids and chromosome 1 ParB proteins from Burkholderiales are indicated as outgroups. Protein and parS variations allow identification of 13 Bsr subtypes. Each subtype is exemplified (right) by one replicon: B. cenocepacia J2315 plasmid pBC (J2315-pBC), B. cenocepacia J2315 chromosome 2 (J2315-c2), B. cenocepacia J2315 chromosome 3 (J2315-c3), P. naphthalenivorans CJ2 plasmid 1 (pNAP1), P. naphthalenivorans CJ2 plasmid 2 (pNAP2), plasmid integrated in chromosome 1 of R. pickettii 12J (12J-c1::p), R. pickettii 12D plasmid 1 (12D-p1), B. vietnamiensis G4 plasmid 2 (G4-p2), R. solanacearum GMI 1000 megaplasmid (Rsol-Mp), Polaromonas sp. strain JS666 plasmid 1 (JS666-p1), Polaromonas sp. strain JS666 plasmid 2 (JS666-p2), R. ferrireducens T118 plasmid 1 (T118-p1), and Burkholderia glumae BGR1 plasmid 4 (BGR1-p4). The minimal 14-bp palindrome (parS) near the parAB operon is indicated. In the case of pNAP1 parS, underlined letters indicate positions of degeneracy. The structure of each parAB operon is shown (black line, minimal palindrome; first arrow, parA; second arrow, parB). ParA proteins vary from 217 residues (BGR1-p4) to 242 (JS666-p2), and ParB proteins vary from 290 (J2315-pBC) to 376 (JS666-p2).