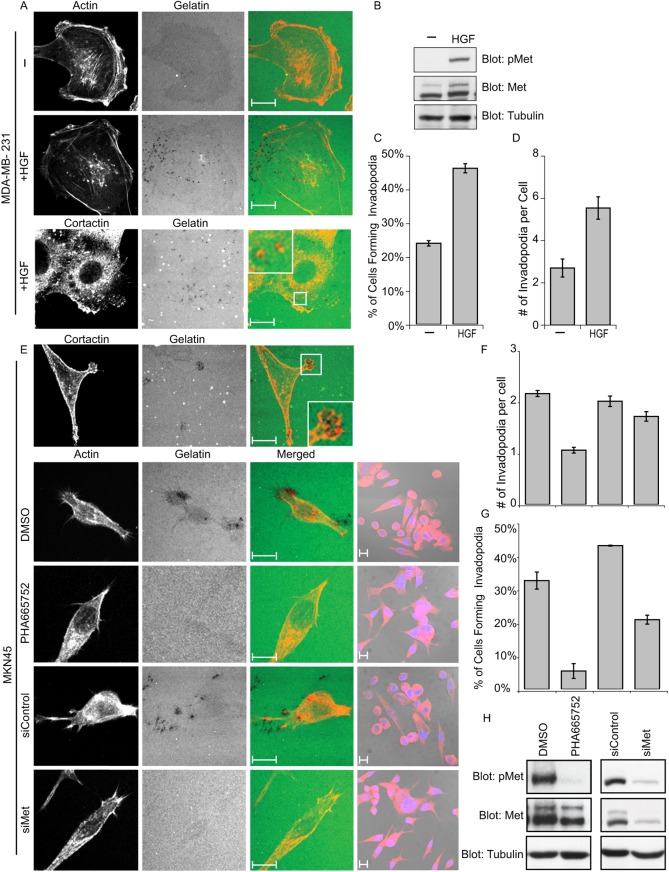
Fig. 2.
Invasive breast cancer cells, MDA-MB-231, and gastric cancer cells, MKN45, form invadopodia in response to Met RTK signaling. (A) MDA-MB-231 cells were cultured on gelatin matrix for 3 hours and stimulated with 0.5 nM HGF for an additional 3 hours. Cells were stained for the invadopodia markers actin (phalloidin) or cortactin. (B) SDS-PAGE was performed on cell lysates of MDA-MB-231 cells stimulated with 0.5 nM HGF and non-stimulated cells. (C,D) The ability of MDA-MB-231 cells to form invadopodia in response to HGF stimulation was quantified. Values are the means of three independent experiments. (E) MKN45 cells were cultured on gelatin matrix in the presence of 0.1 µM Met inhibitor PHA665752 or DMSO for 24 hours. MKN45 cells were treated with 50 nM siRNA targeting Met or control siRNA. Cells were trypsinized 48 hours after treatment and plated on gelatin matrix and cultured for an additional 24 hours. Cells were stained for markers of invadopodia, actin (phalloidin) or cortactin and confocal images were acquired at the ventral plane of the cells. DIC images of cells stained with actin (red) and DAPI (blue) taken at a lower magnification (63×) are shown on the right. Representative images are shown. (F,G) The loss of invadopodia formation in MKN45 cells in response to treatment with Met inhibitor PHA665752 or siRNA-mediated knockdown of Met. (H) SDS-PAGE was performed on cell lysates of MKN45 cells treated with 0.1 µM Met inhibitor or 50 nM siRNA to Met or the respective vehicles (DMSO) or control siRNA and probed for Met-P (pMet), Met and tubulin. Scale bars: 10 μm.