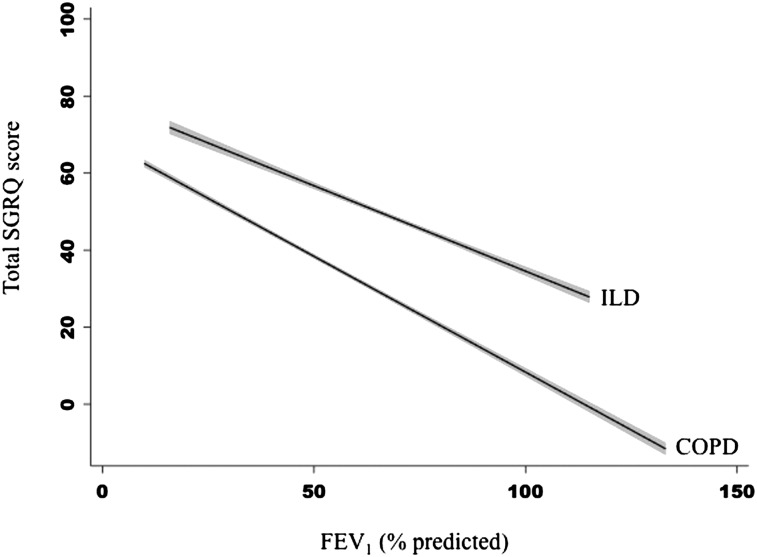
Figure 1.
Slope of the adjusted relationship between FEV1 % predicted and SGRQ score varies by diagnosis. Participants with ILD on average had higher SGRQ scores, indicating worse HRQL compared with those with COPD with similar degrees of ventilatory impairment. However, the slope of the relationship between SGRQ score and FEV1 % predicted was steeper in COPD, indicating greater differences in HRQL for similar differences in FEV1 % predicted in COPD compared with ILD. The gray area around the fitted lines indicates the 95% CI around the estimate. HRQL = health-related quality of life; ILD = interstitial lung disease; SGRQ = St. George Respiratory Questionnaire.