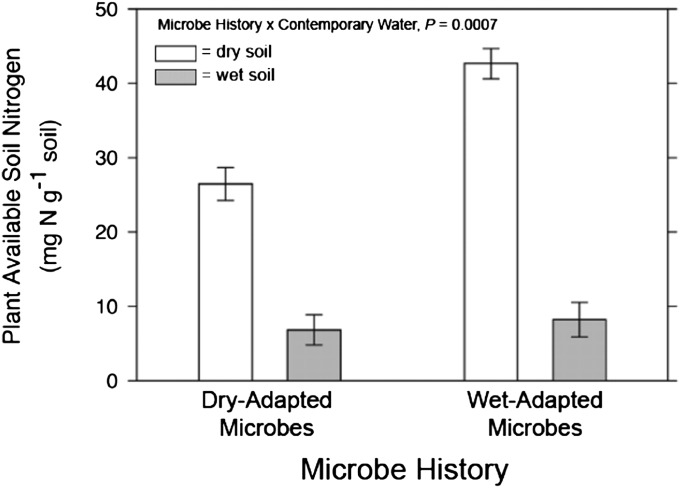
Fig. 3.
Microbe history and contemporary soil moisture (dry, white bars; wet, gray bars) altered plant-available soil N (NH4+ and NO3−). Plant-available N was higher in dry contemporary soil-moisture treatments than in wet contemporary soil-moisture treatments, especially for soils containing a wet-adapted microbial community (microbe history × contemporary moisture, F1,8 = 29.04, P = 0.0007). Error bars indicate least squares means ± 1 SEM.