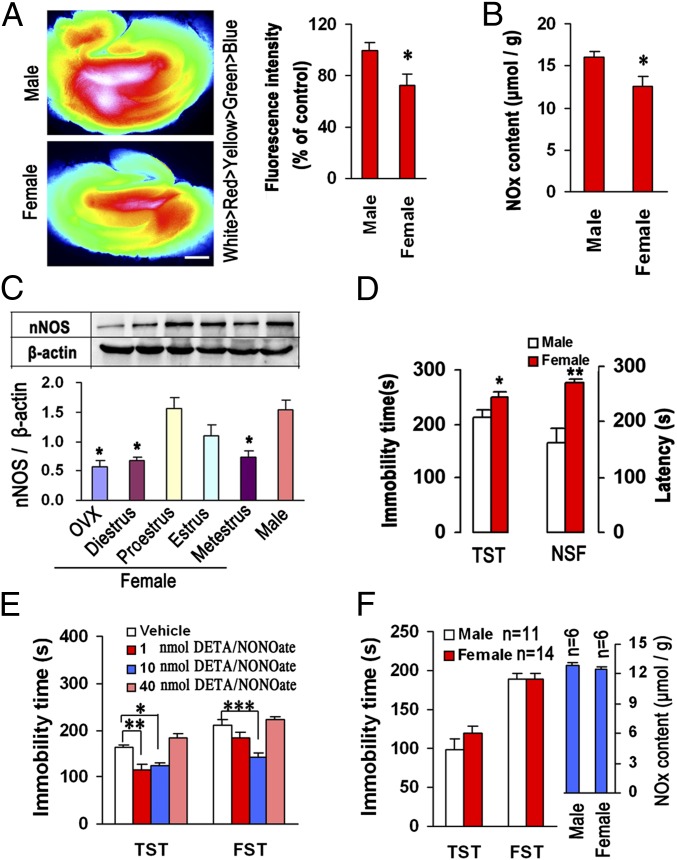
Fig. 1.
Hippocampal NO is crucial for sex differences in affective behaviors. (A) Fluorescence images of a cultured rat hippocampal slice loaded with an NO-sensitive fluorescent dye, 3-Amino, 4-aminomethyl-2′,7′-difluorofluorescein Diacetate (DAF-FM DA). Fluorescence intensity shown in pseudocolor (Left), and a statistical graph showing relative fluorescence intensity (Right) (n = 4). For females, one mouse each stage in estrous cycle. (Scale bar, 400 μm.) (B) NOx contents in male and female hippocampus (n = 9; for female, diestrus, proestrus, or metestrus stage, n = 2, estrus stage, n = 3). (C) Immunoblots showing hippocampal nNOS levels in male or the female mice being within an estrus cycle or subjected to OVX (n = 3). (D) Immobility in the TST and latency in the NSF test in male and female mice (n = 10; for female, diestrus or proestrus stage, n = 2, metestrus or estrus stage, n = 3). (E) Immobility in the TST and FST for the DETA/NONOate-treated OVX-female mice (intrahippocampal infusion, n = 12). (F) Immobility in the TST and FST and hippocampal NOx contents in male and 10 nmol DETA/NONOate-treated OVX-female mice (intrahippocampal infusion). Means ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 in A–D, compared with male.