Figure 7. Intraperitoneal infection of C57Bl/6 mice with MHV68-73TRN mutants reveals mLANA DNA-binding/transcriptional repression function is essential for reactivation from splenocytes.
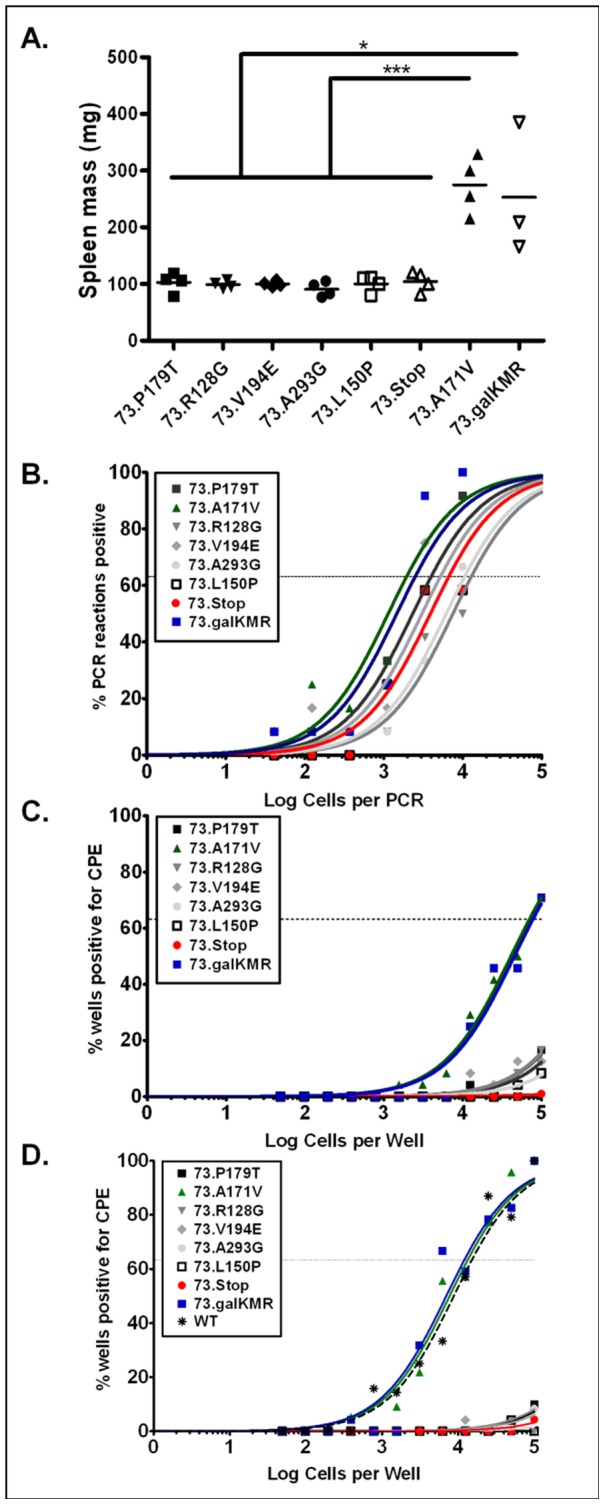
Groups of 3–4 mice were infected intraperitoneally with 1000 PFU of each MHV68-73TRN virus. Eighteen days post-infection mice were sacrificed, and (A) spleens were weighed, (B) the frequency of infected splenocytes was determined by limiting-dilution PCR, and (C) the frequency of cells that reactivate virus was determined by the limiting-dilution CPE assay. In all cases the MHV68-73TRN viruses behaved similar to the mLANA null mutant 73.Stop. (D) Similarly, mice infected intranasally with 1000 PFU each virus were assayed for cells reactivating virus 18 days post infection. *, P<0.05, ***, P<0.001.
